The Graph: A Journey to Revolutionize Data Accessibility
Paradox of Plenty: The Need for Innovation in Blockchain Data
TL;DR
Blockchain technology drives innovation across various industries through decentralization but faces limitations due to low accessibility, hindering explosive growth.
While some providers use centralized APIs to address this, The Graph has gained attention for more efficiently solving it with a decentralized ecosystem.
The Graph enhances blockchain data use by 1) strengthening decentralization, 2) boosting scalability via Arbitrum migration, and 3) adopting AI technology. These efforts aim to improve blockchain accessibility and promote industry development.
1. Hidden Issues of Blockchain Decentralization: “Accessibility”
Blockchain technology, based on decentralization, is driving innovation across various industries. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain distributes data ownership to individuals, significantly enhancing personal 'Data Sovereignty.' Additionally, blockchain offers an open infrastructure where all activities are transparently recorded, further increasing reliability.
However, blockchain technology alone has clear limitations in achieving true data sovereignty. As a decentralized database, blockchain provides only basic functionalities. This creates a challenging environment for developers to utilize it effectively for application development. In other words, blockchain has low technical accessibility. Specifically, there are difficulties in collecting, processing, and utilizing decentralized data, which manifest in the following three specific forms.
1.1. Hard-to-Read Formats
Firstly, blockchain data is in a Bytecode format that is difficult for humans to read and requires processing. As shown in the above figure, transaction data for NFT transfers consists of Bytecode, which must be decoded using the Contract Application Binary Interface(ABI) to be interpreted into a language that people can understand. This necessitates additional tools for accessing, interpreting, and utilizing the data, making user interaction challenging.
1.2. Fragmented Data
Secondly, blockchain data is fragmented, making it challenging to derive meaningful information from it alone. Therefore, collecting and combining fragmented data is essential. For instance, to verify DEX transaction history, it is necessary to gather transaction data and integrate it with other data like DEX-related smart contracts and token prices. This process is crucial for extracting meaningful information from blockchain data.
1.3. Myriads of Data
Lastly, the sheer volume of blockchain data can be overwhelming. Extracting, transforming, and loading the necessary data consumes significant time and resources. Moreover, the size of archive nodes, which store the state of every block for each chain, continues to grow over time. For example, the Solana archive node is approximately 100TB. Additionally, each chain can generate over a million transactions per day, requiring substantial resources for storage and processing. These challenges make the effective utilization of blockchain technology difficult.
2. The Graph: Revolutionizing Blockchain Data Accessibility
To achieve digital innovation across various industries, enhancing 'technical accessibility' is crucial. This is especially important in the technology-intensive blockchain sector. As technical accessibility improves, more developers can leverage blockchain technology to create diverse applications. Ultimately, this expansion in application will accelerate the mass adoption of blockchain technology.
“The Graph” is a protocol designed to enhance the accessibility of blockchain technology. The Graph is a blockchain data indexing protocol that facilitates easier access to decentralized data. Indexing involves organizing data in a structured manner within a database to quickly locate information. The Graph applies this indexing process to the blockchain environment, enabling developers to efficiently use data. In simple terms, The Graph acts as an 'Open API' service for blockchain data, allowing developers to quickly utilize blockchain technology without a deep understanding of it.
For example, suppose you want to implement a service that shows the current ownership status of 'Azuki' NFT project using The Graph. Traditionally, you would need to run nodes to collect and process the transaction data of Azuki NFTs. The Graph eliminates this step. By utilizing 'Subgraph,' a data specification provided by various indexing participants in The Graph, you can easily access well-organized data to implement the service. Additionally, The Graph uses 'GraphQL,' a familiar API standard for web2 developers, making data requests and responses more convenient.
3. What Makes The Graph Different?
The accessibility issues of blockchain have already been pointed out by many, and several blockchain solution providers like Alchemy and Moralis have offered centralized API services to address these issues. However, The Graph has garnered significant attention by taking a different approach, building a decentralized ecosystem to solve these issues more efficiently.
3.1. Solving Dependency Issues Through Decentralization
The Graph effectively addresses the dependency issues of centralized solution providers by operating a decentralized, blockchain-based ecosystem. It mitigates problems like single points of failure through a distributed system, enhancing data accuracy and reliability.
In the web3 ecosystem, similar to web2, dependency issues can frequently occur. This can be particularly critical in finance-related services. For example, a recent technical error at ‘Berkshire Class A’ stock incorrectly showed a 99.9% price drop, highlighting the potential severity of such issues.
In contrast, The Graph creates a balanced environment based on a decentralized ecosystem and resolves these issues through consensus mechanisms. This approach increases the reliability and accuracy of data.
3.2. Transparent Reward System
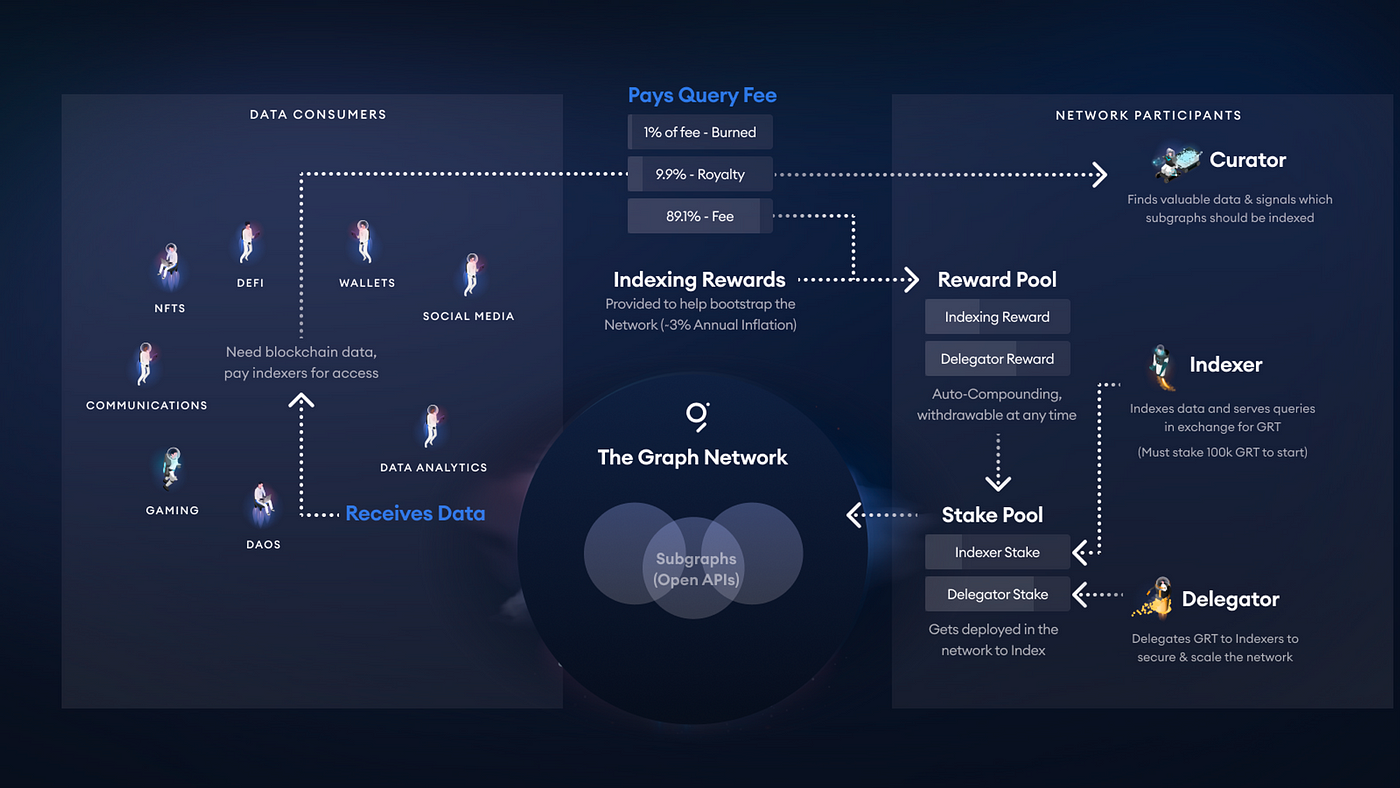
The Graph provides efficient data indexing services within a decentralized environment through a transparent reward system. It maintains a balanced ecosystem by clearly defining the roles of each stakeholder. The Graph ecosystem consists of four main participants:
Indexer: Indexers operate The Graph network nodes and are responsible for data indexing. They index blockchain data based on data specifications known as 'Subgraph' and respond to query requests from data consumers.
Data Consumer: These are the actual data users who utilize blockchain-related data to run their services. They pay fees for queries and can easily access the data.
Curator: Curators evaluate the quality of Subgraphs and recommend those that would be beneficial for both indexers and data consumers. Indexers can perform data indexing based on curators' recommendations, and curators earn incentives for their recommendations.
Delegator: Delegators support indexers by enabling them to perform more tasks and receive a portion of the rewards earned by indexers.
Indexers perform data indexing to earn rewards, and data consumers pay fees to access the data. Curators earn fees by recommending high-quality Subgraphs to indexers, and delegators support indexers' activities and share in their rewards. This reward structure encourages voluntary participation from ecosystem members and enhances diversity and development through balanced ecosystem operations.
3.3. Open Market Innovation
The Graph adopts an 'open market' model, allowing various participants to freely contribute to the ecosystem. This approach maximizes the overall value and efficiency of the ecosystem. As more participants join, the value of the ecosystem increases, creating a flywheel effect that attracts even more users. This open market model fosters innovation, promotes diverse contributions, and enhances the robustness and growth of The Graph's ecosystem.
The Graph distinguishes itself from centralized solution providers like Alchemy and Moralis by offering a more diverse and rich variety of data through its open market model. For example, The Graph can index and provide complex data such as liquidity information from Uniswap v3. This enhances data accessibility and diversity, maximizing the innovation potential. By doing so, The Graph's open market model boosts the scalability of its ecosystem.
4. Additional Innovations by The Graph
The Graph has already contributed to the development of the ecosystem by improving blockchain data accessibility. Looking ahead, it aims to further maximize the potential of blockchain technology through various innovations. Here are three key initiatives that The Graph is set to introduce:
4.1. Fully Decentralized Network
While The Graph has operated a decentralized ecosystem, it has faced centralization risks due to reliance on a small number of indexers. Specifically, the core team, Edge & Node, managed centralized hosting services. However, in October 2022, The Graph announced plans to transition to a fully decentralized network. This transition is structured into three stages—Sunset, Sunbeam, and Sunrise—to safely phase out the hosting service. The final phase of this transition is set to be completed by June 12th 2024, with the ecosystem leveraging over 150 community indexers to strengthen its decentralization. This shift will significantly enhance the trustworthiness and security of The Graph's ecosystem.
4.2. Enhanced Scalability
Initially, The Graph was based on the Ethereum network but faced scalability limitations due to network congestion and high transaction fees. To address this, The Graph pursued chain expansion to Arbitrum. Since the announcement in June 2022, indexers have been migrating to Arbitrum.
The expansion to Arbitrum has alleviated the burden of high network fees for indexers, enabling smoother operations. Delegators and curators have also benefited from lower fees, resulting in more active participation in the network and enhancing The Graph’s overall scalability.
Additionally, The Graph has further strengthened network scalability through the Migration Infrastructure Providers (MIP) program. This program integrates new chains into the network and encourages indexers to support these chains. Through the MIP program, six new chains—Arbitrum, Avalanche, Celo, Fantom, Gnosis, and Polygon—have been onboarded. This expansion goes beyond EVM-compatible chains to include non-EVM chains, with over 50 mainnets now supported.
The MIP program has provided funding to indexers for testing and optimizing support for new chains, significantly improving network performance and scalability. By supporting a diverse range of chains, The Graph’s scalability has been greatly enhanced, allowing it to accommodate more data sources and network participants.
4.3. Integration of AI Technology
Interest in AI technology has surged recently, highlighting the growing importance of AI and the data that fuels the technology. In line with this trend, The Graph, a data-centric project, has announced its AI narrative and is joining the rapidly growing AI industry. By incorporating AI technology, The Graph aims not only to enhance data accessibility but also to drive innovation across the blockchain industry.
The core development team of The Graph, Semiotic Labs, has proposed AI services for The Graph protocol and published a new whitepaper unveiling two AI-based services.
The first is the 'Inference Service.' This service focuses on executing AI models and deriving results. Interestingly, just as The Graph efficiently indexes blockchain data in a decentralized environment, it supports the use of distributed indexers' computing power for deploying and running AI models. This decentralized approach is crucial, especially as the AI industry becomes increasingly centralized around a few large LLMs.
The second is the 'Agent Service.' Built on the Inference Service, it aims to provide natural language experiences similar to ChatGPT. Combined with The Graph's data infrastructure, it is expected to automate complex blockchain technologies and improve the user experience in the existing web3 industry. For example, Semiotic Labs has released a demo version of the SQL agent service named 'Agentc.' This service provides convenient features such as automatically generating on-chain related SQL queries based on natural language and visualizing the results.
Combining various agents to perform specific tasks can result in more diverse applications. For example, you can use Uniswap data to develop optimized liquidity pool strategies or analyze posts and comments on the web3 SNS Farcaster to create popular content.
As The Graph integrates AI technology, it is expected to showcase various AI-based innovations, opening new possibilities for the blockchain industry. By combining AI and data, The Graph has built an efficient pipeline that significantly reduces costs and development time. Similar to how AI has accelerated software development and creative activities, this integration will allow more users to leverage blockchain technology. Furthermore, it is anticipated that innovative use cases across various industries will increase.
The Graph's three initiatives are poised to play a crucial role in driving blockchain industry innovation. Additionally, with plans such as 'Horizon' to further innovate The Graph network, these advancements are expected to continue well into the future.
5. Conclusion
The Graph is not only innovating blockchain data infrastructure but also making impressive strides toward mass adoption. Notably, it supports eight research and development (R&D) teams through its R&D fund. These teams contribute to the growth and advancement of The Graph ecosystem by developing technologies that enable faster and more efficient data indexing. Additionally, new innovations through AI technology, such as those from Semiotic Labs, are also underway.
The activities of indexers, who are key participants in The Graph ecosystem, are also noteworthy. They contribute to the ecosystem in various ways beyond data indexing and querying. For instance, the 'Index Africa' team, one of over 150 community indexers, demonstrates social responsibility by donating a portion of their indexing rewards to nonprofit partners.
The Graph's commitment to continuous communication with its community is also impressive. The Graph Forum serves as a platform where various ecosystem participants actively exchange ideas and engage in discussions. These efforts have significantly contributed to The Graph's development so far, and it is expected to continue playing a crucial role in promoting the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology.
Take a quick, 1-minute survey to enhance the weekly insights we provide. In return, get immediate access to the updated "2024 Country Crypto Matrix" by Tiger Research, featuring the latest global virtual asset market trends. Your participation helps us provide valuable content while you gain cutting-edge analysis.
Disclaimer
This report was partially funded by The Graph. It was independently produced by our researchers using credible sources. The findings, recommendations, and opinions are based on information available at publication time and may change without notice. We disclaim liability for any losses from using this report or its contents and do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. The information may differ from others' views. This report is for informational purposes only and is not legal, business, investment, or tax advice. References to securities or digital assets are for illustration only, not investment advice or offers. This material is not intended for investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn't harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research's reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state 'Tiger Research' as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo, and 3) incorporate the original link to the report. If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.