This report was written by Tiger Research, examining Orbiter Finance's evolution from a secure cross-chain bridge to an omnichain infrastructure provider with its Vizing Layer 2 solution.
TL;DR
Bridges enable cross-chain asset transfers but remain vulnerable to security threats. Orbiter Finance has operated securely since 2021, earning user trust.
With the rise of new chains and DeFi expansion, the bridge market is growing rapidly, with annual asset transfers projected to reach $510.7 billion by 2027. Fast integrations, technical stability, and low fees are key to capturing market share.
Building on a robust product, Orbiter Finance is expanding beyond bridges with ‘Vizing’, aiming to revolutionize cross-chain asset and data transfers through omnichain infrastructure.
1. The OG of the Bridge Market You Need to Know
The cryptocurrency market has seen numerous projects rise and fall, and blockchain bridges are no exception. As a critical component of the ecosystem, bridges facilitate asset transfers between different blockchains, serving as a simple connectivity tool.
A bridge is a specialized protocol that connects two distinct blockchains economically, technically, and conceptually. Similar to a physical bridge, it goes beyond simple connectivity by enabling the swift and efficient transfer of assets between networks. As multiple Layer 2 (L2) solutions continue to emerge, bridges have become essential for integrating fragmented ecosystems.
Contrary to their significance, bridges are frequently exposed to severe security risks. A notable example is the Wormhole Bridge hack, where attackers exploited a vulnerability in Wormhole’s Solana smart contract, forged a fake signature, and fraudulently issued 120,000 $wETH. These tokens were then exchanged for real $ETH on the Ethereum network, resulting in substantial losses. A compromised bridge disrupts multiple networks, much like a collapsed physical bridge affecting two connected cities.
Bridges are prime targets for hackers due to the substantial funds they manage and their reliance on trust mechanisms encoded in smart contracts. Coordinating different blockchain rules introduces vulnerabilities, while limited validator nodes heighten the risk of key theft. Even in decentralized environments designed to minimize trust dependencies, human oversight remains a critical security challenge.
Despite security risks, bridges are essential to the cryptocurrency market. Nonethelss, evaluating projects that have demonstrated sustained stability is crucial to maintain healthy activity in the space. Orbiter Finance, for instance, has operated its bridge service since 2021—a considerable period in the fast-moving Web3 industry. The platform has maintained steady growth and user trust, distinguishing itself through operational resilience.
Orbiter Finance received early support from prominent investors, including Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and OKX Ventures. This report will analyze how Orbiter Finance has established a competitive edge in the bridge market and assess its future prospects.
2. What is the most important thing about the growing bridge market?
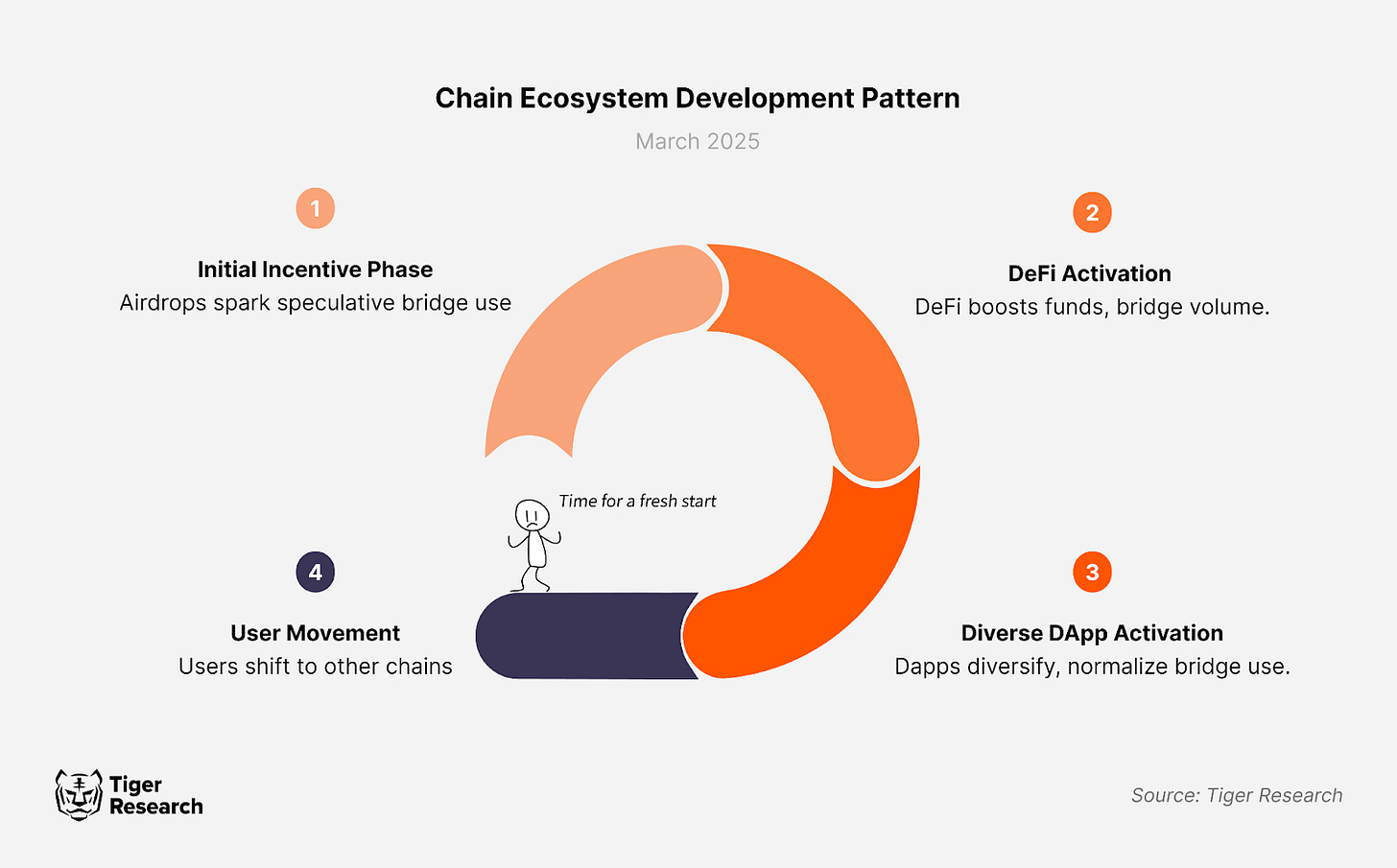
The blockchain ecosystem is constantly growing. New chains are constantly emerging. In this process, the bridge market is also benefiting from the continuous development pattern of the chain ecosystem.
Initial Incentive: When a new chain launches, incentives such as airdrops attract investor interest. The anticipation of rewards drives investors to transfer assets to the new chain via bridge protocols, initiating bridge usage.
DeFi Activation: Beyond airdrop participation, DeFi services within the chain gain traction. Early inflows find utility across lending, staking, and liquidity provision in various DeFi protocols, further attracting additional capital. As cross-chain asset movement increases, bridge transaction volumes rise significantly.
Diverse DApp Activation: As the ecosystem develops, new DApps such as gaming platforms and NFT marketplaces emerge, driving further capital inflows. At this stage, bridge usage becomes a routine component of the ecosystem.
However, as new chains emerge, attention constantly shifts to new ecosystems, and the demand for bridges increases once again. In other words, the market for bridges grows as new chains emerge and the ecosystem matures.
This shift resembles the migration of merchants from established shopping districts to newly developed ones. As older districts become gentrified and less profitable, new districts offer lower rents, early-mover advantages, and potential long-term value appreciation. Early entrants often gain priority access to future opportunities, such as franchising benefits. These compounded incentives drive a continuous cycle of retail migration. This is representative of the movement of capital across blockchain ecosystems as a whole.
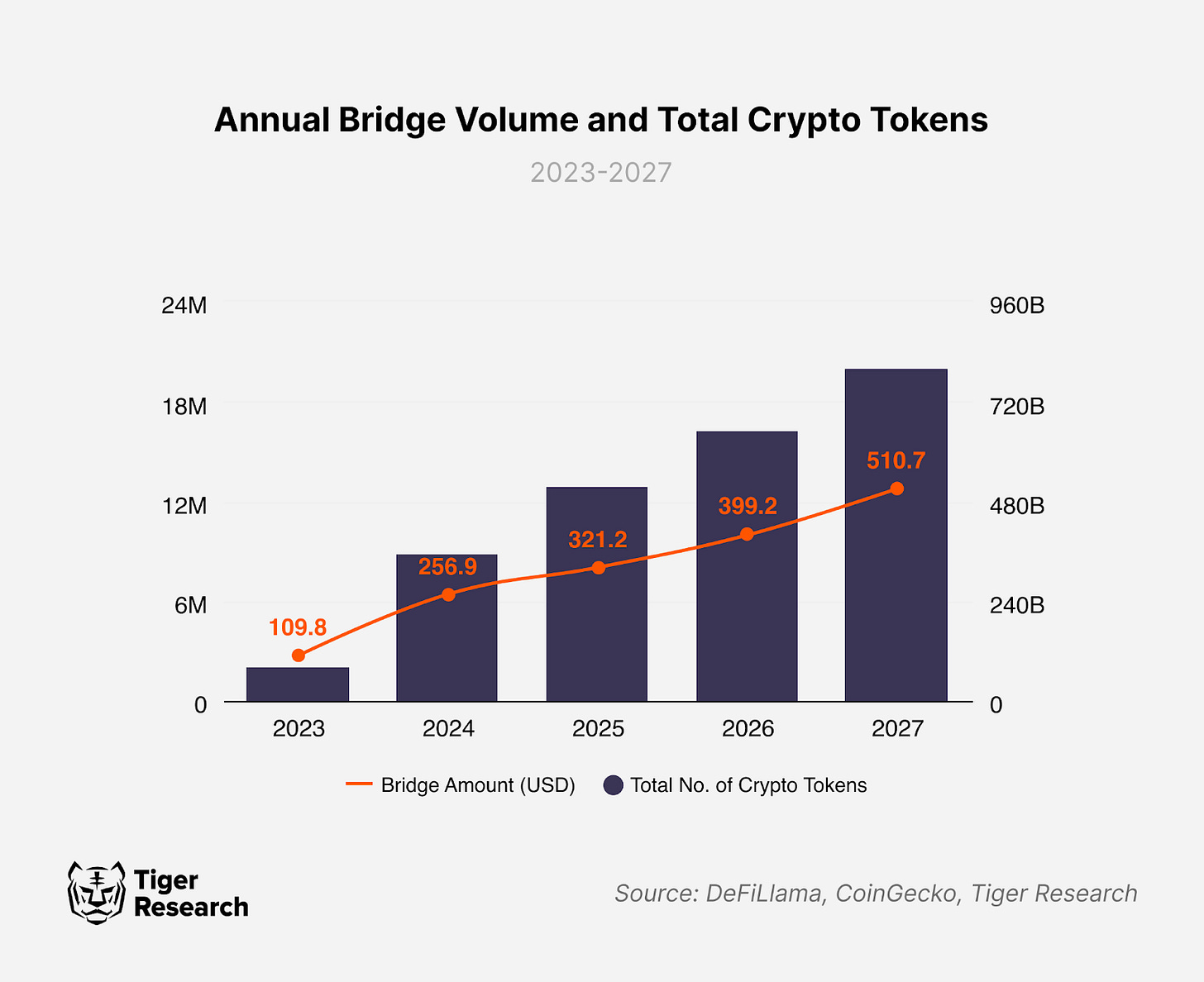
According to DeFiLlama, annual asset bridging reached $256.9 billion in 2024. This is more than double the amount from 2023. However, this figure does not account for all chains, suggesting that the actual bridging volume is likely higher.
This growth has been accompanied by notable market shifts. The blockchain ecosystem is maturing, with rapidly expanding regulatory frameworks. Additionally, the introduction of memecoin launchpads has driven a surge in token projects, though the number of high-quality projects remains limited relative to overall growth. Given these conditions, the annual bridged asset volume is conservatively projected to reach $510.7 billion by 2027.
In this expanding bridge market, securing stable fee revenue and a strong market position depends on three critical factors. First, the ability to swiftly establish connections with emerging chains. Second, ensuring a technically robust and secure service. Lastly, offering competitive transaction speeds and low fees. These factors are essential for maintaining and expanding market share.
In this market environment, Orbiter Finance is uniquely positioned as a decentralized bridge that enables the movement of assets between various networks. Its scalability to quickly connect new and emerging projects such as Abstract and Story, as well as major projects such as Solana, is a key factor in the continued influx of users, especially with its fast transfer speeds of 10-20 seconds and low fees.
With this superior technology and scalability, Orbiter has succeeded in simplifying the movement of blockchain assets in the growing bridge market indistinguishable from the level of everyday online transactions. This in turn completes the "bridge between Web2 and Web3" role, further solidifying Orbiter Finance's unique position in the rapidly evolving blockchain market.
2.1. Orbiter’s Push for New Chain Connectivity
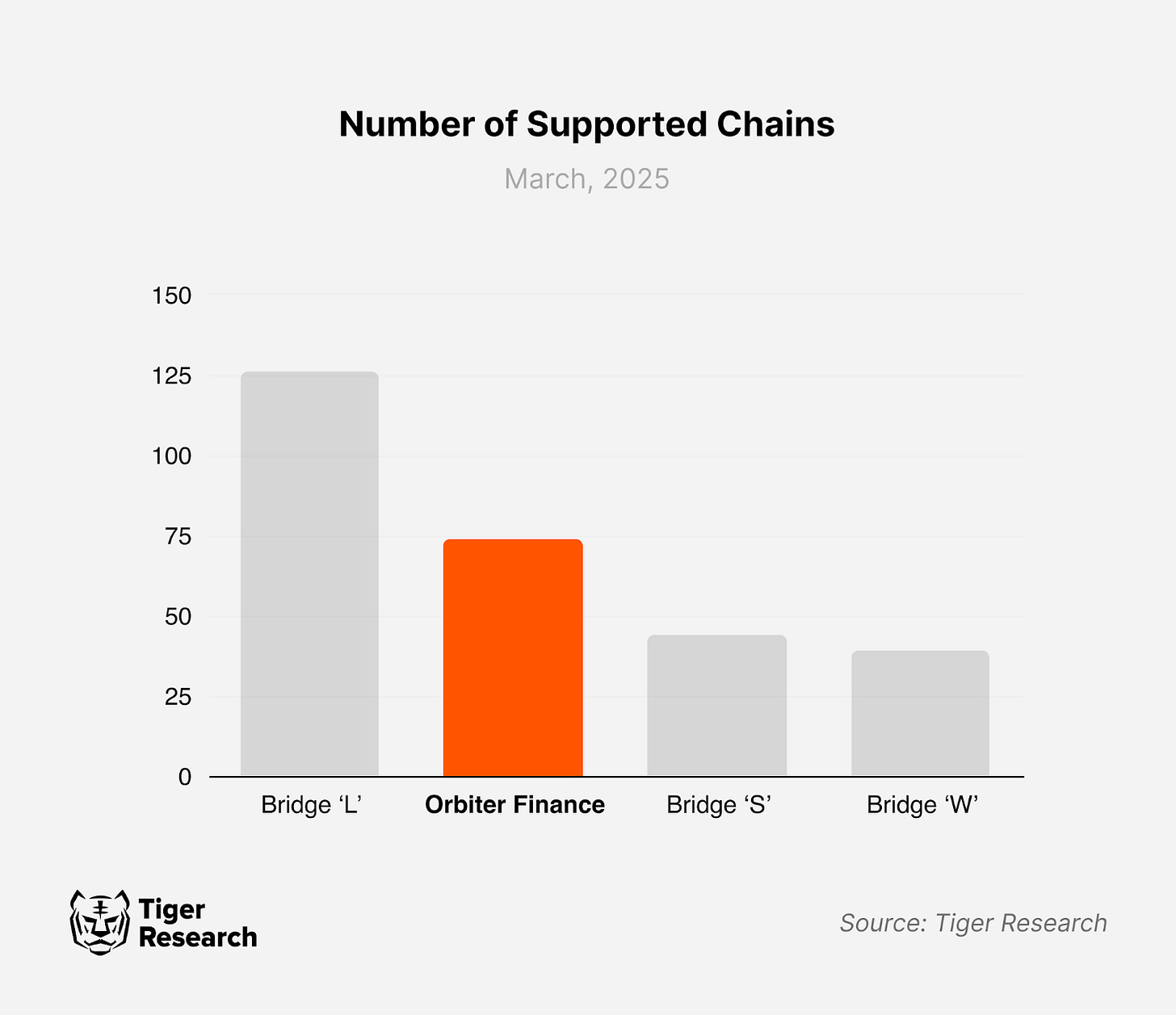
Orbiter Finance supports over 70 blockchains, rapidly expanding its coverage by integrating highly scalable new chains. Its most distinctive strength lies in its swift adoption of the latest Ethereum L2 solutions. Among the various L2 rollups designed to address Ethereum’s scalability challenges, Orbiter Finance has been particularly proactive in integrating rollups utilizing zero-knowledge (ZK) technology.
Orbiter Finance strengthens its position in the ZK ecosystem by integrating ZK-based chains like ZKFair, zkLink Nova, and Proof of Play Apex. It has also expanded within the Ethereum ecosystem by developing Vizing, its proprietary ZK-based L2 network. It also supports a wide range of L2 solutions, including Arbitrum and Optimism, facilitating seamless interoperability between Ethereum-based L2 networks.
Another key differentiator is Orbiter Finance’s early integration of Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions. While most bridge services have yet to support Bitcoin-based chains, Orbiter Finance has taken the lead in integrating networks such as BEVM, Bitlayer, and B² Network. This approach indicates Orbiter’s drive to incorporate ecosystems beyond Ethereum, reaching OG ecosystems like Bitcoin. This offers users greater flexibility in asset transfers.
These strategies position Orbiter Finance as a bridge provider leveraging the rapid expansion of Ethereum’s L2 ecosystem while maintaining flexibility and interoperability across multiple Layer 1 (L1) blockchains. As Ethereum’s L2 adoption accelerates, Orbiter Finance is poised to play an increasingly influential role in cross-chain connectivity.
2.2. Technically reliable service
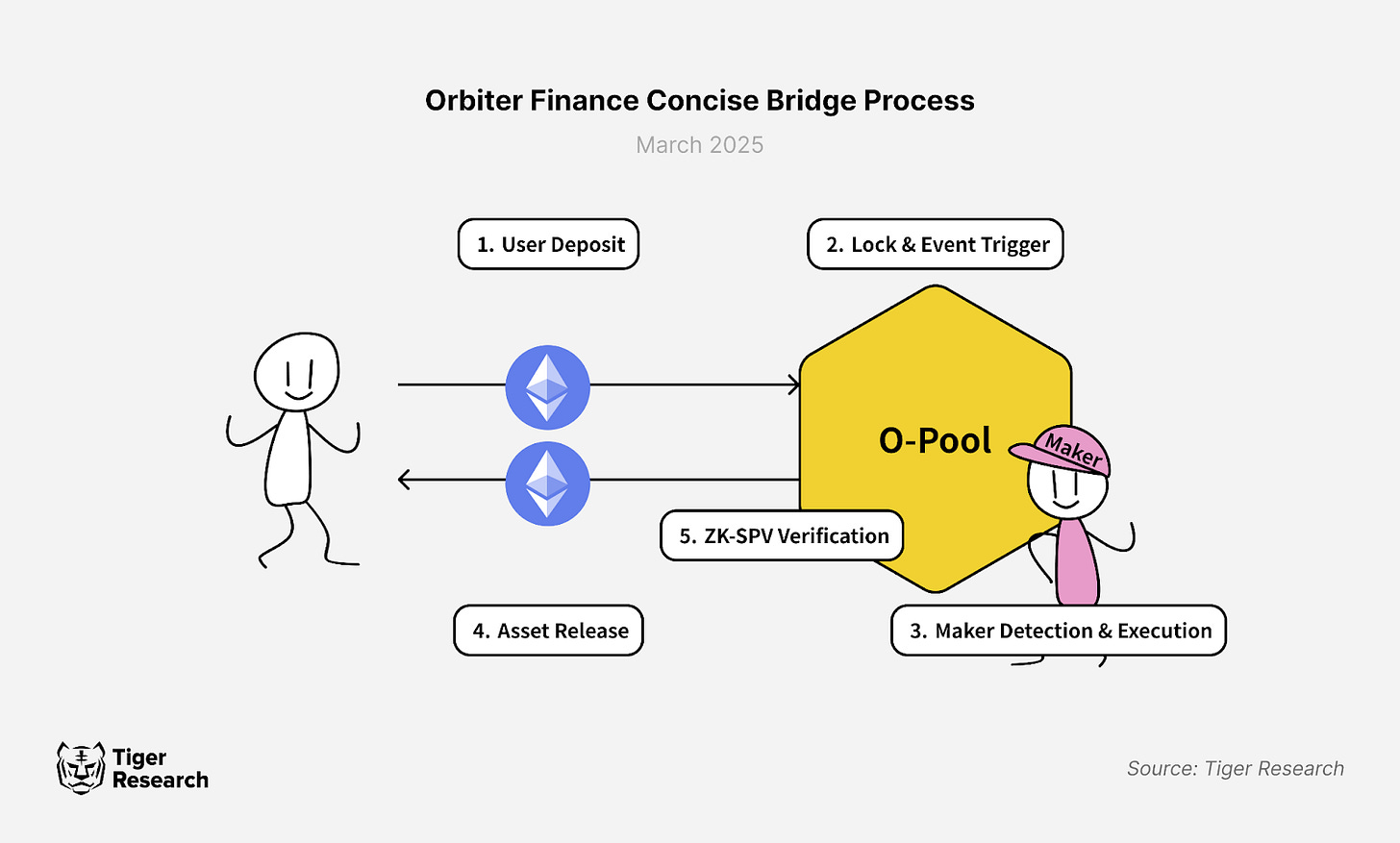
Since 2021, Orbiter Finance has maintained a stable bridge service without security incidents. As a cross-chain bridge that combines a decentralized maker network with smart contract-based liquidity pools, it ensures both security and efficiency through its ZK-SPV technology and O-Pool system.
Orbiter Finance operates on a straightforward mechanism. When a user deposits assets into the O-Pool contract on the source chain for bridging, a maker node detects the transaction and facilitates the transfer of the same asset from the O-Pool on the destination chain. In this process, makers earn fees, while ZK-SPV cryptographically verifies the legitimacy of the transaction, ensuring secure and trust-minimized cross-chain transfers.
The system functions similarly to a network of banks operating across multiple countries. When a user deposits funds in a bank within one country (the origin chain), a bank representative (maker) notifies a branch in another country (the destination chain) to provide the equivalent amount. All transactions are reinforced through an unforgeable receipt (ZK proof), ensuring security and trust.
From a technical perspective, Orbiter Finance integrates two key components. First, the O-Pool system manages liquidity using smart contracts deployed across multiple chains. Users deposit assets into the O-Pool through the source chain, and maker nodes detect and facilitate withdrawals on the destination chain. Second, ZK-SPV technology leverages zero-knowledge proofs to mathematically verify cross-chain transactions, enabling instant validation without extended waiting periods. This eliminates the latency challenges associated with optimistic verification methods.
This model represents a significant advancement in cross-chain infrastructure. Rather than relying on centralized mechanisms such as wrapped token issuance or multi-signature validators, Orbiter Finance employs a decentralized maker model that does not rely on complicated wrapping processes for efficiency and stability, combined with ZK-SPV technology to enhance security. This approach establishes a trust-minimized and scalable framework for seamless asset transfers across blockchain ecosystems.
2.3. Competitive speed and fee rates
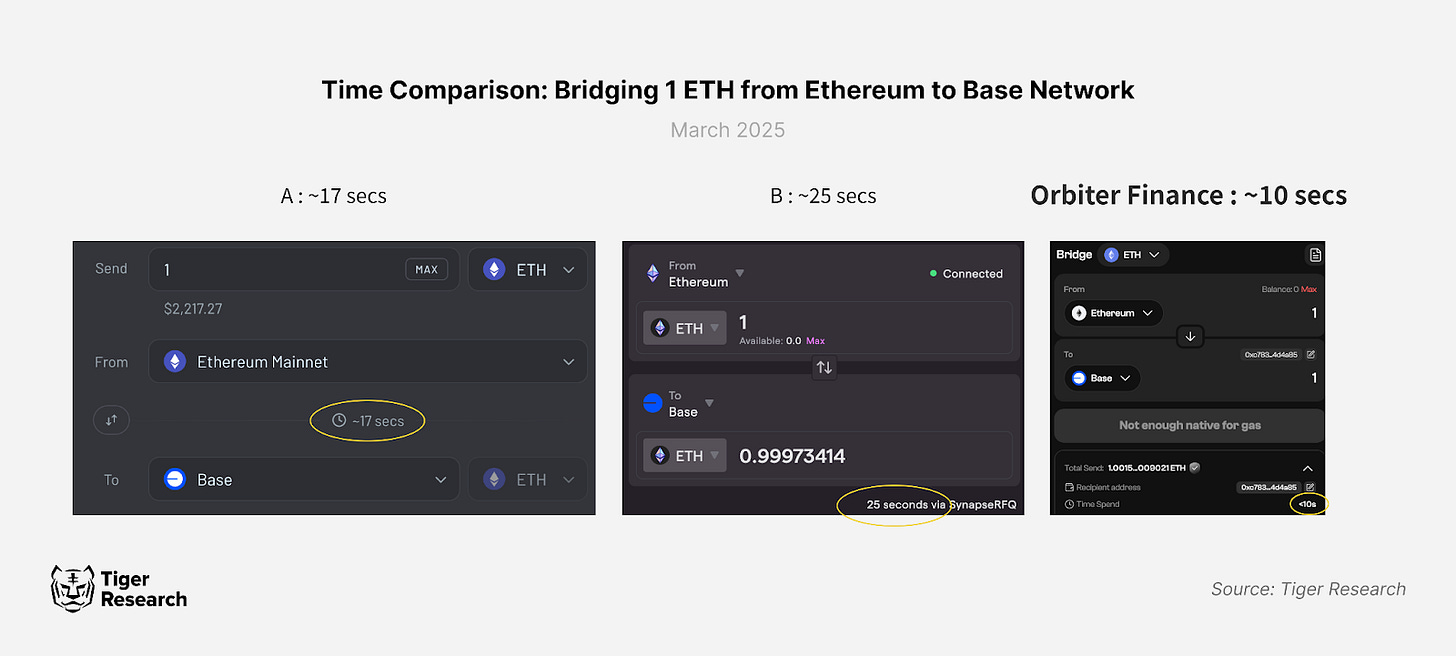
Orbiter Finance offers industry-leading transaction speeds, with cross-chain transfers typically completing within 10 to 20 seconds—a notable advantage compared to other bridge services. This speed advantage is primarily driven by its ZK-SPV technology and streamlined transfer mechanism, which minimizes block confirmations required for execution.
In addition to speed, Orbiter Finance demonstrates strong fee efficiency, particularly for L2 transfers. By minimizing smart contract calls, the platform reduces gas consumption for ETH bridging to approximately 21,000 gas, significantly lower than competing bridges which consume 120,000 to 450,000 gas per transaction. However, while Orbiter Finance generally maintains a cost advantage, its fee structure is not uniformly superior across all routes. In certain market conditions and specific transfer paths, its fees may be higher than those of competitors.
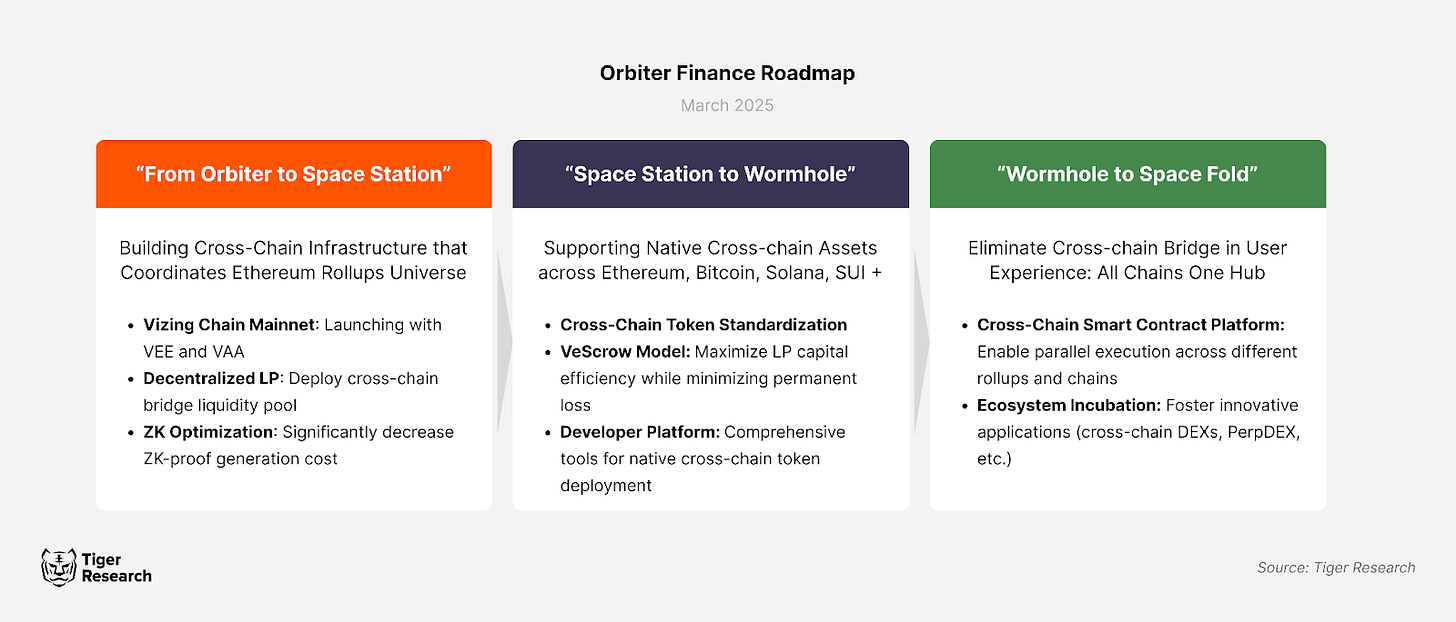
3. Vizing, the vision of Orbiter Finance
Orbiter Finance aims to go beyond providing a simple bridge service by expanding interoperability in a L2-centric environment. Traditional cross-chain solutions have primarily focused on asset transfers, but as blockchain ecosystems evolve, demand for cross-chain messaging and data transmission is increasing.
This shift is similar to the development of urban infrastructure—moving beyond roads to include communication networks and utility systems. For instance, a DeFi application on one chain may need to call a price oracle from another chain or execute transactions based on specific events occurring elsewhere. However, existing bridge systems face limitations in efficiently handling such cross-chain data interactions.
To address this, Orbiter Finance has developed Vizing, a ZK-based Ethereum Layer 2 network designed to support on-chain messaging and cross-chain data transfers. Vizing enables faster and more efficient movement of assets and data across chains through leveraging zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) for data verification.
Vizing has two core strengths. First, Vizing Account Abstraction (VAA) allows users to manage multiple Layer 2 networks with a single account, significantly improving convenience. Second, Vizing Environment Layer (VEL) provides a consistent execution environment across all Layer 2s, enabling developers to deploy applications across multiple chains with a single implementation.
Vizing is currently focused on addressing key challenges in Layer 2 interoperability. To support ecosystem growth, a grant program was launched last year, marking its first major step toward adoption.
A notable example is Likwid, an AMM-based service leveraging Vizing’s technology. Likwid enables fully decentralized derivatives trading without centralized intermediaries. Recognized by Uniswap as a DeFi Innovation Champion, it has created an environment where derivatives can be traded without oracles or counterparties.
By enabling cross-chain communication and data sharing beyond simple asset transfers, Vizing addresses fragmentation within the Layer 2 ecosystem. This improves the efficiency and usability of blockchain infrastructure, laying a foundation for broader real-world applications of blockchain technology.
4. Orbiter Finance. A Faster, Stronger Ecosystem
Ethereum's challenges extend beyond simple liquidity fragmentation. While the number of L2 solutions continues to grow, Ethereum's fundamental scalability and performance improvements have been slow. The network's transaction processing capacity remains limited, prompting the development of auxiliary networks. However, these efforts have not resulted in a fundamental increase in throughput.
For example, when User A on Base transfers 1 ETH to User B on Arbitrum, the current Ethereum L2 environment still requires reading data from L1 and updating Ethereum’s state on the Beacon Chain. As the central ledger of Ethereum 2.0, the Beacon Chain manages the final record and validation of all transactions. This structure makes L2 scalability dependent on L1 performance, creating a bottleneck.
This situation is analogous to sending money from Seoul to Busan, where all transactions must be processed through the central bank. Even if the number of local banks (L2s) increases, the overall system remains constrained if the central bank (L1) processes transactions slowly.
To address these limitations, Orbiter Finance is developing an infrastructure that enables direct rollup-to-rollup communication. This Omnichain Infrastructure removes barriers between blockchain networks, facilitating seamless asset transfers and data exchange while reducing dependency on Ethereum L1. By allowing L2 liquidity to be shared as a collective resource, Orbiter aims to increase efficiency across the Ethereum ecosystem.
Key components of this infrastructure include:
Omnichain Wallet System: A unified account system that minimizes L1 data access, similar to a universal bank account number. Regardless of which local bank (L2) a user interacts with, they can access funds through a single account, reducing the need for L1 verification.
Relayer Protocol: A cross-shard communication protocol that enables rollups to act as direct intermediaries, bypassing L1 for transactions. This is akin to a direct banking network that allows Busan and Daegu banks to transact without routing through the Seoul central bank.
Liquidity Aggregation Layer: A liquidity management system that pools assets across chains. Similar to a shared liquidity pool for regional banks, this ensures that funds from different networks can be dynamically allocated where needed, improving capital efficiency.
Parallel Execution Contracts: Omnichain smart contracts that are automatically deployed across all rollups, similar to Vizing Dapps. This model eliminates the need to separately develop financial products for each bank, enabling seamless deployment across all networks.
By implementing this model, Ethereum L1 can focus on security, while L2s handle execution and transactions, eliminating bottlenecks without compromising decentralization. This shift mirrors a financial system where central banks oversee stability and policy, while regional banks manage day-to-day transactions independently.
Rather than removing L1 (the central bank), Orbiter Finance’s Omnichain Infrastructure alleviates existing bottlenecks by allowing direct L2-to-L2 transfers. The result is a more efficient financial network, where local banks (L2s) handle transactions autonomously, while the central bank (L1) intervenes only when necessary. This model fosters collaboration among rollups, shifting the industry away from TVL competition and toward a more decentralized and scalable ecosystem.
5. A Vision Built on a Strong Foundation
Orbiter Finance has built a solid foundation in its core business. By offering fast and differentiated chain integrations, a technically stable infrastructure, and cost-effective transactions, it provides a reliable bridge service to real users, securing a strong active user base.
At the same time, the company presents a rational and well-grounded vision for the future. As the L2 ecosystem expands, Orbiter Finance has identified key scalability challenges and is systematically developing solutions to address them.
Unlike competitors that focus on unrealized visions, Orbiter Finance leverages a working service and an active user base to expand Vizing, methodically broadening its business scope. This strategic approach not only secures a stable market share in the growing bridge sector but also creates additional revenue opportunities in new markets.
As L2 ecosystems mature and DeFi services expand, the role of bridges and omnichain infrastructure will become even more critical. For instance, users will increasingly seek to combine Arbitrum’s high-yield lending services with Optimism’s efficiency, or utilize staked assets on Base for derivatives trading on Scroll. Just as traditional finance has evolved through complex financial products and strategies, cross-chain asset movement and multi-layered DeFi strategies will become commonplace. As this shift accelerates, bridge services and omnichain infrastructure like Orbiter Finance will become indispensable components of the blockchain ecosystem.
However, continuous monitoring is essential to assess the stability of Vizing’s ecosystem services. While Likwid has been launched, it remains in its early stages and requires further adoption to demonstrate its full potential. Additionally, there is always a gap between vision and execution, making it crucial to closely track the roadmap’s implementation progress.
🐯 More from Tiger Research
Read more reports related to this research.The Great Era of RaaS: Caldera Opens a New Age of Exploration
Lumoz: Decentralized Compute Infrastructure for the Era of AI, ZK & RaaS
Disclaimer
This report was partially funded by Orbiter Finance. It was independently produced by our researchers using credible sources. The findings, recommendations, and opinions are based on information available at publication time and may change without notice. We disclaim liability for any losses from using this report or its contents and do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. The information may differ from others' views. This report is for informational purposes only and is not legal, business, investment, or tax advice. References to securities or digital assets are for illustration only, not investment advice or offers. This material is not intended for investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn't harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research's reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state 'Tiger Research' as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo(Black/White). If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.