SOON: For the community, by the community, of the community
Decoupled SVM: Breaking the Boundaries of Blockchain
This report was written by Tiger Research, examining SOON's innovative Decoupled SVM technology and its groundbreaking approach to community-driven blockchain development, featuring a 51% token allocation to the community.
TL;DR
Industry-first true community-driven project with 51% token allocation to community, backed by Solana ecosystem leaders
Innovative Decoupled SVM technology separates Solana Virtual Machine from consensus layer, enabling deployment across any blockchain network
Comprehensive ecosystem solution including SOON Stack for L1s to build SVM-based L2s and InterSOON protocol bridging multiple chains, demonstrated by $150M TON-Solana bridge volume
1. Redefining Community-Driven Growth: SOON's New Approach
Decentralization is a fundamental principle of blockchain technology. However, the full implementation of decentralization remains challenging. Most projects now adopt hybrid approaches that incorporate centralized elements to optimize operational efficiency.
This shift largely stems from blockchain projects' dependence on attention-driven market dynamics, or the ‘Attention Economy’. Success requires support from industry leaders who can attract retail investor interest. To secure this backing, early-stage projects typically offer venture capital firms and key industry figures discounted token allocations.
As mentioned in our previous report, this strategy extends to Fair Launch platforms. While promoting equitable token distribution, these platforms use whitelist features to offer early sales and distributions at preferred prices unavailable to retail investors to accounts expected to provide significant value. This practice has raised questions about whether these launches truly uphold fairness principles.
Projects must balance fairness with the need for strategic industry support, as the current environment differs markedly from the organic growth seen in the early ICO era. As projects today depend heavily on “endorsement” from established market leaders, managing fair token distribution remains challenging. Many early token purchasers with founding team connections fail to deliver their promised strategic value post-sale.
The SOON project introduces a distinctive approach within current industry practices. Their presales for research and content production offered retail participants nearly identical terms for purchasing 'COMMing SOON NFT' as other buyers. This strategy reimagines the fair distribution principles established by successful projects such as Solana, Polkadot, and Avalanche, adapting them for 2024 market conditions.
SOON project advanced decentralization efforts by implementing a tokenomics model that allocates 51% of total tokens to the community. Going beyond marketing, this allocation demonstrates a concrete commitment to community-driven governance.
This implementation succeeded through three factors: founder credibility, industry leader support for SOON's community-centric vision, and strong technical infrastructure. This report examines SOON's execution of this community-focused strategy.
2. Trust in SOON’s Key Figures and Industry Leaders
Joanna Zeng, SOON's co-founder and CEO, brings extensive blockchain experience since 2017, having held leadership roles at Aleo, Optimism Foundation, and Coinbase. Combined with her 13-year career at Citibank, her expertise spans both Web3 and traditional finance. This places her in an ideal position as a founder to bridge these sectors.
SOON has established strong connections within the Solana ecosystem, securing support from influential figures including Solana Labs' Yakovenko (Toly), Solana Foundation's Lily Liu, Coinbase's Jonathan King, and Celestia's Mustafa Al-Bassam. This backing reflects both Zeng's industry track record and SOON's anticipated impact on the Solana ecosystem.
The backing from Solana ecosystem leaders carries unique significance, rooted in their shared experience through market challenges, particularly when SOL traded at $8. Their support extends beyond typical KOL or VC endorsements and likely provided SOON with the foundation to pursue community-based fundraising without discounted token allocations to VCs and KOLs despite the current competitive landscape.
3. SOON's Expansion of Blockchain Boundaries
Given how many blockchain projects have gained attention but failed to sustain momentum, understanding SOON's technological foundation and its supporters' technical capabilities is essential.
SOON's core initiative is developing the Super Adoption Stack (SAS), a high-performance SVM (Solana Virtual Machine) roll-up platform that enables seamless cross-network communication and interaction, targeting blockchain mass adoption.
SOON pursues two primary objectives: 1) Deploying the high-performance SVM execution layer across all Layer 1 (L1) networks, including Ethereum. 2) Creating a platform for seamless interaction between L1 and SVM-based chains.
Despite the proven efficiency of the SVM execution layer, discussions continue about implementation approaches. Nonetheless, the Solana ecosystem is banking on SVM's potential through its rapidly growing number of initiatives. Extending this execution layer to other L1s would allow projects to build ecosystems quickly, choosing L1s based on security needs and cost considerations.
This approach liberates projects from ecosystem constraints while expanding development possibilities. Cross-ecosystem connectivity enables both asset transfers and development efficiency, supporting broader blockchain adoption.
SOON advances these goals through three core components: SOON Stack, SOON Mainnet, and InterSOON. Since its June 2024 launch, the ecosystem has rapidly achieved key milestones - SOON Devnet release, Testnet launch, and Mainnet Alpha - outpacing typical development timelines where the mainnet alpha phase often faces delays.
3.1. SOON Mainnet
3.1.1. Decoupled SVM
SOON mainnet introduces 'Decoupled SVM', the first architecture separating Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) from its original consensus layer, implemented as an Ethereum Layer 2 solution. SVM, a high-performance execution environment, was previously bound to Solana's consensus mechanism - much like a high-performance engine fixed to one specific car chassis, unable to power other vehicles.
Solana's original SVM architecture featured tightly coupled execution and consensus layers. Each transaction required processing through Proof of History (PoH) and Tower BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance) consensus mechanisms. PoH maintained chronological transaction ordering, similar to a dated newspaper archive. This system allowed Solana to process transactions in a predetermined sequence, unlike traditional blockchains that needed to adjust transaction orders individually during block creation.
Tower BFT validated these ordered transactions through progressive validator voting on new blocks, contrasting with traditional blockchains' requirement for simultaneous validation from all validators. While this approach achieved faster consensus, the architecture restricted SVM to Solana's blockchain, This prevented independent operation or integration with other blockchain networks.
In Solana's original architecture, state changes - including token transfers, smart contract executions, and NFT minting - required validation through both PoH and Tower BFT consensus mechanisms before being recorded on the network.
SOON overcomes these limitations by decoupling SVM from Solana's consensus layer, creating a standalone execution environment. The platform preserves data integrity through a new architecture that processes transactions independently of Solana's consensus requirements. It stores SVM transaction data in a separate data availability (DA) layer and links execution results to an Ethereum-based verification system. Using a verification process similar to Optimism Fault Proof, the system enables independent validation of SVM execution results with dispute resolution capabilities.
SOON's innovation enables SVM deployment across blockchain networks without single-chain dependency. This advancement goes beyond decoupling from Solana, representing a complete redesign of verification and data availability systems to achieve both scalability and flexibility. By adapting Solana's execution environment for Ethereum and other networks, SOON's separation of consensus and execution layers opens possibilities beyond traditional blockchain constraints.
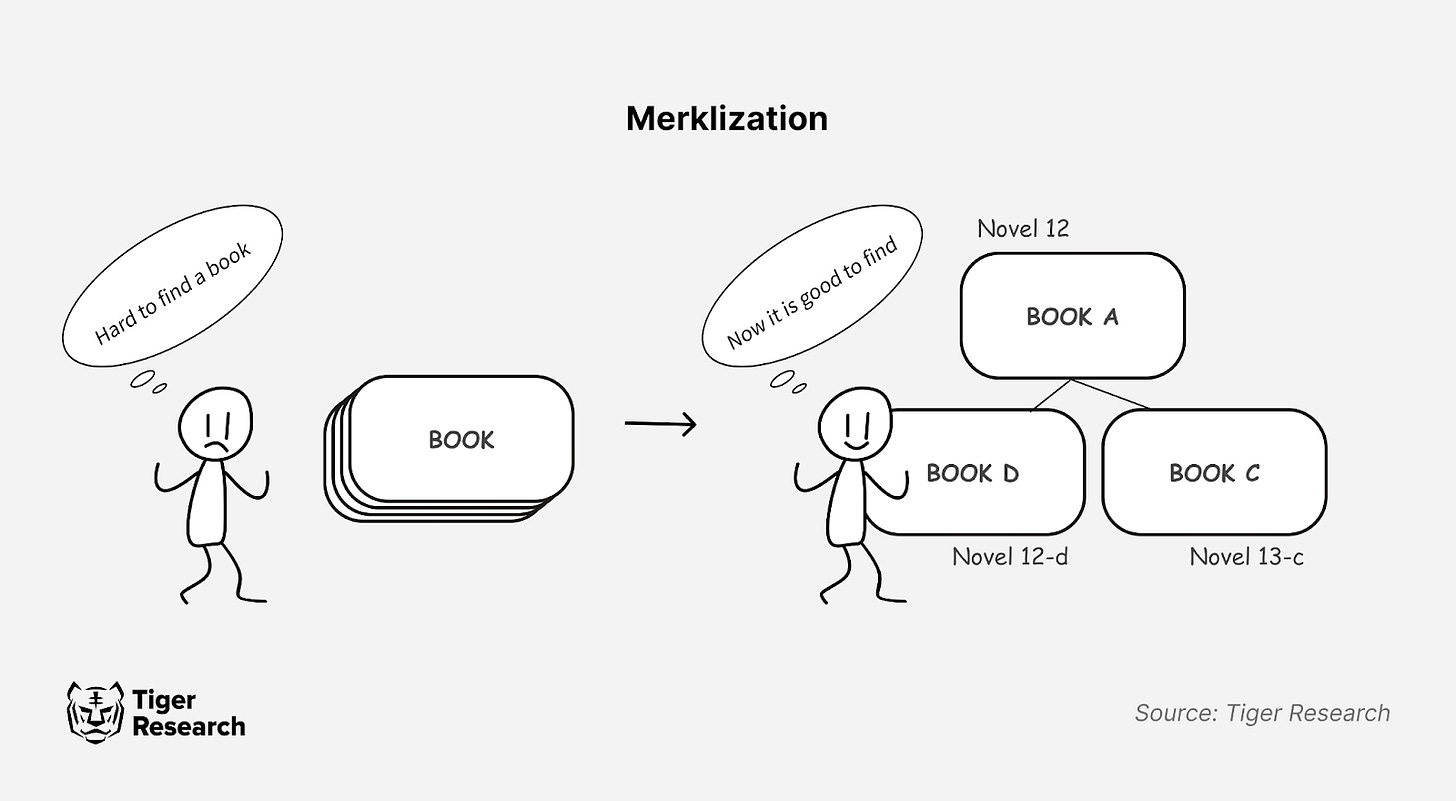
3.1.2. Merklization
SOON implements Merklization to overcome Solana's structural limitations, improving blockchain reliability and scalability. Merklization creates an organized data structure for efficient verification, similar to how a library index system allows users to quickly locate books without having to search through every shelf.
Solana's original design prioritized transaction speed, but this optimization came with a key trade-off: no Global State Root. Without this unified state reference point, transaction verification required extensive data recalculation. This limitation made cross-chain rollup solutions difficult to implement - similar to a library lacking a catalog, where locating a specific book requires searching every shelf manually.
SOON adapts Ethereum's Merkle Patricia Trie (MPT) state management system for Solana's architecture. This implementation consolidates transactions and account states into a single Merkle root for efficient verification. The Merklized data enables lightweight client validation without requiring full network state downloads, similar to how mobile banking lets users check their account balances without having to access the entire bank database.
Through Merklization, SOON delivers an enhanced Layer 2 solution for Solana with improved verification speed and reliability, while strengthening cross-chain capabilities. This creates scalable infrastructure for blockchain ecosystem expansion and innovation.
3.1.3. Horizontal Scaling
SOON uses horizontal scaling to expand processing capacity by distributing transactions across multiple nodes. When 10 nodes each process 1,000 transactions, the system handles 10,000 transactions simultaneously. This approach proves cost-effective through standard specification nodes and allows unlimited scaling based on demand.
This architecture also enhances network resilience, as the system maintains operations even when individual nodes face disruptions. Through these innovations, SOON mainnet achieves 50-millisecond block times and processes over 30,000 transactions per second. The platform extends to various L1 ecosystems through multiple data availability solutions, including eigenDA.
3.2. SOON Stack
SOON Stack is a technical framework that enables L1 blockchains to build their own SVM Layer 2 solutions. This framework holds a similar position to Arbitrum Nitro or Optimism Bedrock. It leverages technology from SOON Mainnet, the official L2 chain operating on Ethereum.
Its core technology, Decoupled SVM, enables any L1 blockchain to construct Layer 2 solutions with Solana-level performance. This allows chains to implement high-performance execution environments tailored to their specific requirements.
Several implementations demonstrate SOON Stack's practical applications in the field. CARV SVM is optimized for AI applications, Cytonic SVM enables multi-VM ecosystem interoperability, and svmBNB delivers high-performance processing for Binance Smart Chain. These projects maintain stable real-time services through customized gas fee structures aligned with their specific requirements.
SOON is expanding partnerships with key Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) providers, including AltLayer and Caldera, to enhance technical reliability. The team aims to extend support across L1 blockchains and DA solutions.
This comprehensive approach empowers developers to build innovative applications leveraging SVM's capabilities. SOON Stack has evolved beyond a technical platform to establish itself as a crucial driver of blockchain ecosystem scalability.
3.3. InterSOON
InterSOON is a messaging protocol designed to facilitate efficient communication between blockchain networks. One of its most notable achievements is the native bridge connecting TON and Solana, which recorded $150 million in transaction volume within just two months of launch.
Traditional cross-chain transfers suffer from significant inefficiencies. For instance, moving ETH to another blockchain requires locking the original asset in a custodial vault and issuing wrapped tokens on the destination chain. This approach fragments liquidity and adds complexity, reducing capital efficiency.
InterSOON addresses this by using a Hyperlane-based direct messaging system to eliminate intermediaries. Like express delivery services moving packages directly between sender and recipient, messages travel straight from source to destination chain, with real-time validator verification. This enables SOON Mainnet, SOON Stack-based chains, and major blockchain networks to operate as one system.
InterSOON offers three key advantages: a standardized communication framework that lets developers use a single protocol for all cross-chain interactions; preservation of asset integrity through direct transfers without wrapping; and enhanced processing speed with reduced fees through its Decoupled SVM architecture.
These innovations establish true blockchain interoperability, creating a foundation for advanced cross-chain services.
4. SOON’s Ecosystem Strategy: Adaptability and Technological Innovation
SOON has shown notable adaptability in the evolving blockchain landscape. While technical excellence is crucial, sustainable growth requires responding to market trends and industry shifts. SOON demonstrates this flexibility by integrating emerging technologies and building strategic partnerships to expand its ecosystem.
This adaptability is clear in SOON's approach to AI integration. The platform has optimized its infrastructure for AI applications' specific demands of speed, cost efficiency, and data reliability. Projects like CARV, an AI-specialized chain, now build on SOON's foundation. Beyond following AI trends, SOON launched its own AI agent, SOON Girl, showcasing practical implementation.
SOON's adaptability extends to ecosystem growth through strategic partnerships with industry leaders: including Aethir in DePIN, Bonk, EigenLayer, and AltLayer.
By rapidly incorporating major market trends and collaborating with industry-leading projects, SOON continues to position itself at the forefront of blockchain innovation. The project's proven ability to execute and adapt reinforces its industry impact.
5. Growth Through Community Engagement
This report emphasizes SOON's focus on community-driven growth over rapid expansion through select leaders. The project maintains development pace to build community trust and engagement, supporting sustainable growth. The Big Bang ecosystem campaign, launching with February's mainnet release, will boost community involvement by offering $SOON token rewards to NFT holders and users engaging with ecosystem projects.
The success of SOON's blockchain adoption strategy will ultimately be measured by SOON Stack adoption rates. While initial progress is promising, attracting influential flagship projects remains crucial for ecosystem growth. Given the blockchain community's evolving interests, maintaining long-term community trust will be essential for SOON's continued development.
🐯 More from Tiger Research
Read more reports related to this research.Disclaimer
This report was partially funded by SOON. It was independently produced by our researchers using credible sources. The findings, recommendations, and opinions are based on information available at publication time and may change without notice. We disclaim liability for any losses from using this report or its contents and do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. The information may differ from others' views. This report is for informational purposes only and is not legal, business, investment, or tax advice. References to securities or digital assets are for illustration only, not investment advice or offers. This material is not intended for investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn't harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research's reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state 'Tiger Research' as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo(Black/White). If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.