TL;DR
The Web3 industry is dynamic, with numerous mainnet projects appearing and vanishing. Mergers and acquisitions between mainnets are emerging as a new trend.
Mainnet mergers and acquisitions offer benefits like enhancing competitiveness, securing talent, and expanding value. However, caution is necessary due to the vastness of mainnet ecosystems and potential exchange delisting issues.
In the fast-paced Web3 market, mergers and acquisitions may become a key strategy, but using them solely for price manipulation or risk avoidance should be avoided.
1. Introduction
In the Web3 industry, mergers and acquisitions (M&As) between mainnets have recently emerged as a new trend. Each mainnet seeks to generate synergy by merging with others that bring different assets and experiences or to quickly enhance its competitiveness by acquiring a mainnet with proven technological capabilities.
The Web3 industry is characterized by its rapid evolution, with trends emerging, being consumed rapidly, and shifting at an unprecedented pace. Every day, new mainnet projects spring up, and those unable to adapt quickly may find themselves edged out and rendered obsolete. Data from Coingecko reveals that an average of 5,300 new token projects are launched daily, highlighting the fast-paced nature of the market with projects continually appearing and fading away. Although token projects differ from mainnet projects, it is reasonable to suggest that trends within the token project sphere also impact the dynamics of the mainnet market to a certain degree.
As competition in the Web3 industry grows fiercer, mergers and acquisitions (M&As) are emerging as strategic maneuvers for projects to boost their competitiveness and ensure survival. The frequency and variety of M&As between mainnets are anticipated to rise, significantly influencing the industry's developmental trajectory. This report analyzes recent M&A cases among mainnets, delving into the objectives behind these strategies and the expected outcomes they aim to achieve.
2. Mergers and Acquisitions: The New Trend in the Web3 Industry
Recent acquisitions and mergers between mainnets can be categorized into three main strategies. First, there is 1) horizontal integration, where a mainnet project acquires or merges with a competing mainnet within the same market to strengthen its market influence. Next, there is 2) vertical integration, aiming to reduce costs and maximize synergy by merging with a mainnet related to the value chain in a specific business or field. Lastly, 3) conglomerate integration, where mainnets without direct business relevance merge to diversify their operations and quickly enhance capabilities in less experienced areas.
Vertical Integration
May 2023, Vietnam's Coin98 announced the acquisition of TomoChain.
March 2024, SingularityNET announced plans to integrate with Fetch and OceanProtocol.
Horizontal Integration
January 2024, Klaytn announced plans to merge with Finschia.
Conglomerate Integration
April 2024, Carry Protocol announced plans to integrate with SLG.Games.
2.1. 'Kaia': The Integration Project of Klaytn and Finschia Foundation
The merger between Klaytn and the Finschia Foundation represents the first case of a merger between mainnets. In January, the two projects announced plans to launch an integrated mainnet, which has now been rebranded as 'Kaia'. Their goal is to create Asia's No. 1 mega blockchain by combining their ecosystems and assets, aiming to lead the global Web3 market.
This merger is seen as an effort to expand their dominant influence in the Web3 market, especially in Asia, by merging competing mainnets. It is significant as it aims for a comprehensive integration of human, material, and technological resources. Kaia is expected to operate with the combined personnel from Klaytn and the Finschia Foundation, along with the integration of their respective assets. Notable examples include Klaytn's exclusive on-chain assets and real-world assets (RWA), as well as Finschia's LINE FRIENDS IP-based games and other content assets.
Leveraging the expertise of EVM-based Klaytn and Cosmos-based Finschia, the teams plan to develop an integrated mainnet that supports both EVM and CosmWasm compatibility. This initiative is anticipated to create a substantial ecosystem within the Web3 industry, leading to the emergence of a highly advanced mainnet.
Through this comprehensive integration, Klaytn and Finschia will engage in close cooperation to maximize each other’s strengths and address their respective weaknesses. They are also expected to utilize the assets of Kakao and LINE, their cooperative partners, to further solidify their dominance in the Asian market. In the Web3 industry, where institutional investments are increasing and development is accelerating, this merger is considered a timely and strategic move. There is significant anticipation regarding the changes and innovations this merger will introduce to the global Web3 ecosystem, extending beyond Asia.
2.2. Acquisition of Mainnet Technology through Coin98's Acquisition of TomoChain
In May last year, Vietnam's Web3 platform Coin98 acquired the local mainnet TomoChain. This is evaluated as a strategy for Coin98, which lacked experience in mainnet development, to secure technological competitiveness in a short period of time and maximize synergy effects by acquiring TomoChain, which possesses proven technical capabilities.
After acquiring TomoChain, Coin98 rebranded it as Viction, making it a core component of its ecosystem. Coin98 plans to leverage Viction's technology and resources to foster a developer-friendly environment and create synergy by integrating it with various services, such as its Web3 wallet. This integration is anticipated to be a unique strength for Coin98 in the competitive Web3 industry. However, as the changes so far have been primarily cosmetic, including only a ticker change of the native token, it remains to be seen what actual impact this rebranding will have in practice.
Industry attention is focused on the potential changes and influence that the collaboration between Coin98 and TomoChain will bring to the Web3 industry. If this acquisition successfully integrates and leverages both entities' strengths, it is expected to establish a new model for securing mainnet technology and expanding the ecosystem.
2.3. Birth of the Web3 AI Alliance's Mega Project 'ASI'
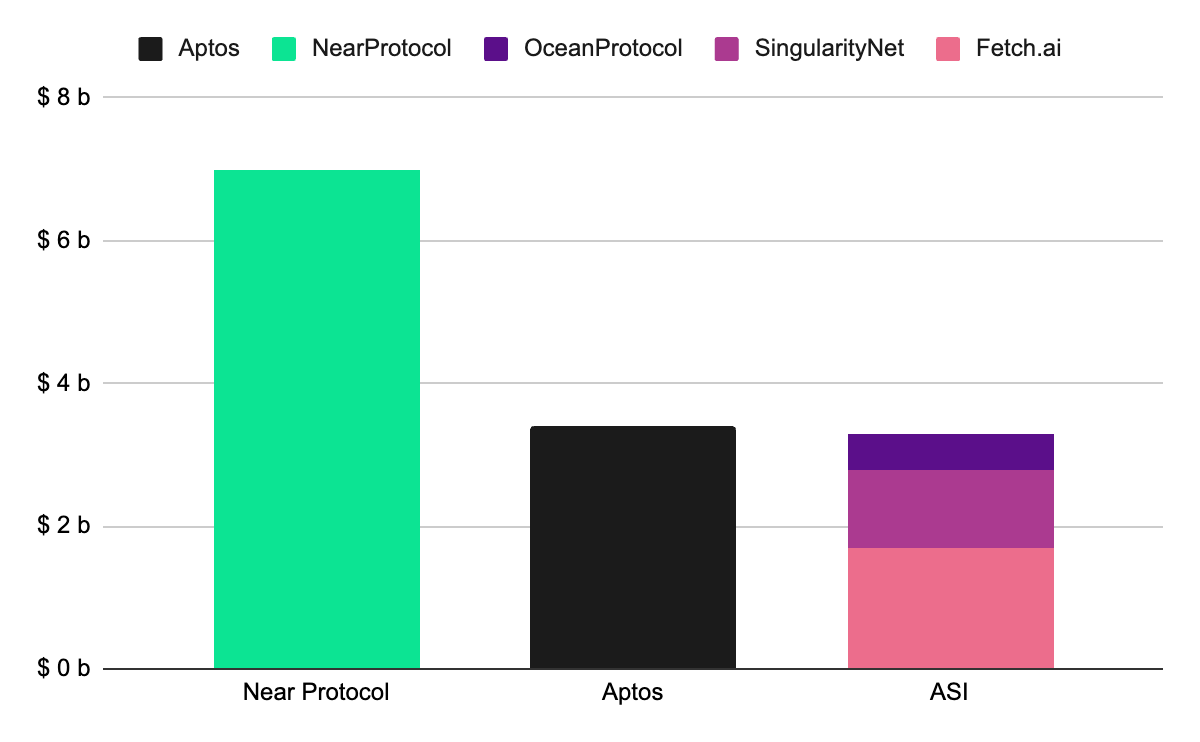
In March, Web3 projects in the artificial intelligence sector—SingularityNET, Fetch, and Ocean Protocol—announced their merger plans. With the governance vote approved in April, they are set to launch a new token project called 'ASI (Artificial SuperIntelligence)'. This merger differs slightly from the integration of Klaytn and Finschia, as they are creating a new project to expand their initiatives while preserving the independence of each foundation.
The projects involved in the ASI initiative are not direct competitors but rather complementary projects connected to the value chain of the artificial intelligence industry through vertical integration. They plan to consolidate their existing tokens into ASI tokens and vertically integrate the technology stacks from each project using a Cosmos-based chain that is a hard fork of the Fetch mainnet. The primary objective is to create synergy and accelerate the development of decentralized AI technology.
The projects participating in the ASI project are not direct competitors but rather a combination of projects connected to the value chain of the artificial intelligence industry, strongly characterized by vertical integration. They plan to merge their existing tokens into ASI tokens and vertically integrate the technology stacks held by each project using a Cosmos-based chain that is a hard fork of the Fetch mainnet. The goal is to create synergy and accelerate the development of decentralized AI technology.
Meanwhile, the leadership, teams, communities, and treasuries of each foundation involved in the ASI project are expected to remain unchanged. This approach is more akin to a strategic partnership rather than a complete merger, indicating an intention to create synergy through collaboration while preserving the identity and distinct characteristics of each individual project.
The ASI project aims to spearhead the advancement of Web3-based AI technology through vertical integration in the artificial intelligence sector. By setting goals that would be challenging to achieve as standalone projects, they intend to drive innovation by leveraging the combined strengths of each participating entity. As the convergence of Web3 and AI garners attention as a critical driver of future technological progress, the development of the ASI project is anticipated to become a significant milestone in establishing a decentralized artificial intelligence ecosystem.
2.4. The Convergence of Advertising and Gaming Industries: 'GAME Build' Project's Expansion
In April, Carry Protocol, a blockchain-based rewarded advertising platform, and SLG.Games, a Web3 gaming platform, announced their merger plans. Following a governance vote, they revealed the launch of a new token project called 'Game Build'. By integrating their expertise in blockchain technology, advertising, and game development, they aim to generate synergy and drive innovation within the Web3 gaming ecosystem.
The merger of these two projects exemplifies conglomerate integration, aiming to leverage each other's strengths to complement capabilities in relatively lacking areas. Carry Protocol plans to collaborate by utilizing its expertise in blockchain technology and advertising, while SLG.Games will contribute its accumulated know-how in game development and blockchain integration. The objective is to introduce a blockchain-based advertising platform and development tools specialized for the gaming industry. Furthermore, the Game Build project envisions providing advertising solutions optimized for Web3 games and a developer-friendly one-stop infrastructure.
The success of the Game Build project hinges on how effectively Carry Protocol and SLG.Games can merge their respective expertise to create synergy. It will be important to observe the changes and innovations their collaboration brings to the gaming industry.
3. What are the purposes behind the merging of mainnets?
The case studies examined so far reveal that mergers and acquisitions between mainnets are emerging as a notable trend in the Web3 industry. These movements are driven by various objectives, which can be analyzed into three main factors:
Strengthening business and technological competitiveness
Securing specialized talent
External expansion of project value
Firstly, there is the strengthening of business and technological competitiveness. Through mergers and acquisitions, mainnets can expand geographically or enter new business areas. The 'Kaia' project by Klaytn and Finschia exemplifies this strategy. Klaytn and Finschia have competitive strengths in different regions and business areas, with Klaytn excelling in infrastructure-based industries and Finschia in content-based industries. Their merger aims to broaden their respective business areas, address weaknesses, accelerate growth and development, and rapidly increase market share.
Moreover, it can also be a strategic move for technological advancement. By acquiring a mainnet with specialized technological capabilities, a company can swiftly elevate its own technology. Coin98's acquisition of TomoChain serves as a prime example. Their goal is to secure advanced mainnet technology through this acquisition and expand their wallet ecosystem. This approach is efficient in terms of both time and cost, making it a crucial strategy in the competitive Web3 industry.
Secondly, there is the goal of securing specialized talent. The Web3 industry is a rapidly evolving and cutting-edge technology sector where acquiring capable talent significantly impacts a project's growth and development. In particular, individuals with experience in directly designing and developing mainnets, such as blockchain core developers, are in short supply. According to a 2023 survey by Stack Overflow, only 0.42% of all developers are blockchain developers, indicating a severe shortage of specialized personnel. Therefore, mergers and acquisitions between mainnets are also pursued to secure such valuable talent.
Lastly, there is the goal of externally expanding project value. In the Web3 industry, market capitalization and Total Value Locked (TVL) are critical indicators for evaluating mainnets and are seen as measures of credibility. These metrics significantly enhance a mainnet's brand awareness and strengthen its market position. Projects with higher market capitalization or TVL attract more attention and capital inflow. Consequently, mainnets are adopting strategies to rapidly increase their corporate value externally through mergers and acquisitions. By combining the liquidity and capital of each mainnet, they can quickly boost TVL and fortify their market standing, making mergers and acquisitions an attractive option.
In fact, the merger of three projects—SingularityNET, Fetch, and Ocean Protocol—achieved the milestone of entering the top 30 in market capitalization rapidly. This example demonstrates that mergers and acquisitions can be an effective strategy for accelerating the external growth of mainnets and expanding their influence within the industry.
In this way, mergers and acquisitions between mainnets are becoming a crucial strategy for companies in the Web3 industry to overcome growth limitations and enhance competitiveness. These initiatives, driven by objectives such as expanding business scope, advancing technology, and securing specialized talent, are anticipated to continue and significantly influence the future development of the Web3 industry.
4. What are the points to note in mainnet merger cases?
Mainnet project mergers come with various risks, similar to those encountered in the Web2 industry. Specifically, merging mainnets involves integrating vast ecosystems and cultures, making the process more intricate and requiring careful consideration.
Difficulties in the integration of human and material resources
Difficulties in integrating communities and ecosystems
Problems with exchange listings
Firstly, it is essential to be cautious about the challenges associated with integrating human and material resources. This process mirrors the issues typically encountered in corporate mergers and acquisitions. A notable example is the merger between Benz and Chrysler, often referred to as the "merger of the century," which garnered significant market attention but ultimately failed. The merger suffered due to cultural clashes and differing work methods. Similar issues can arise in mainnet merger cases, necessitating careful management and foresight.
Secondly, integrating communities and ecosystems presents significant challenges. Unlike Web2 companies, mainnets encompass ecosystems and communities that include various dApps and governance participants. Therefore, both internal and external integration with stakeholders is crucial. A notable example is the opposition from the community and governance participants during the merger process of Klaytn and Finschia. Since mainnets operate within a decentralized structure, achieving consensus is essential not only internally but also among the broader ecosystem stakeholders. Therefore, when deciding on a merger, it is critical to ensure a smooth process and recognize that problems may arise if integration is not handled carefully.
For mainnets, having their tokens listed on exchanges is crucial. However, the process of ticker conversions or issuing new integrated tokens during mainnet integration may not proceed smoothly on exchanges. In reality, most exchanges are extremely cautious of ticker conversions and new token issuances resulting from mergers. If delisting occurs, it can take a long time to relist, potentially diminishing competitiveness in the process.
In conclusion, the post-integration process is critical in mergers and acquisitions between mainnets. Unlike Web2 companies, mainnets must secure consensus from a more diverse and complex array of stakeholders and address issues like exchange listings meticulously. Successful mergers and acquisitions between mainnets require well-prepared strategies and implementation plans to navigate these challenges effectively.
5. Conclusion
Mergers and acquisitions between mainnets are anticipated to become the new standard in the Web3 industry. As the number of blockchain projects continues to grow, only a few mainnets will ultimately gain market favor. Consequently, frequent mergers and acquisitions between various projects are expected to address shortcomings and enhance strengths.
However, this process should not be used as an event aimed at short-term price increases or as a means of avoiding responsibility or risk. As seen in the merger case of Klaytn and Finschia, active communication, persuasion, and long-term preparation must precede the process. In most current project mergers, governance voting is poorly conducted, and voter turnout is low. For instance, in the merger proposal between Carry Protocol and SLG.Games, voting was conducted by only about 100 wallet addresses, indicating that the opinions of all token holders were not sufficiently reflected.
Nevertheless, as more cases accumulate and new strategies and narratives are established, these confusing situations are expected to improve. In conclusion, mainnet mergers and acquisitions are crucial strategies for overcoming growth constraints and accelerating development in the dynamic Web3 industry. It is important to observe whether recent merger and acquisition cases can serve as positive precedents.
Take a quick, 1-minute survey to enhance the weekly insights we provide. In return, get immediate access to the updated "2024 Country Crypto Matrix" by Tiger Research, featuring the latest global virtual asset market trends. Your participation helps us provide valuable content while you gain cutting-edge analysis.
Disclaimer
This report has been prepared based on materials believed to be reliable. However, we do not expressly or impliedly warrant the accuracy, completeness, and suitability of the information. We disclaim any liability for any losses arising from the use of this report or its contents. The conclusions and recommendations in this report are based on information available at the time of preparation and are subject to change without notice. All projects, estimates, forecasts, objectives, opinions, and views expressed in this report are subject to change without notice and may differ from or be contrary to the opinions of others or other organizations.
This document is for informational purposes only and should not be considered legal, business, investment, or tax advice. Any references to securities or digital assets are for illustrative purposes only and do not constitute an investment recommendation or an offer to provide investment advisory services. This material is not directed at investors or potential investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn't harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research's reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state 'Tiger Research' as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo, and 3) incorporate the original link to the report. If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.