Bless Network: The New Computing Infrastructure Driving the AI Age
Pioneering the Next-Gen Infra for a Global Computing Grid
This report was written by Tiger Research, analyzing how Bless Network aims to revolutionize computing infrastructure through its distributed edge computing solution for the AI era.
TL;DR
Bless Network delivers a new distributed infrastructure solution to meet explosive AI computing demands. Traditional centralized cloud infrastructure fails to solve critical challenges in stability, accessibility, and cost.
Bless powers its distributed edge computing with idle resources from everyday devices like MacBooks and PCs. The platform ensures stability through automatic orchestration, enhances security with WASM-based isolation, and will cut costs by 90% compared to traditional cloud services.
Bless enables decentralization for blockchain, provides efficient platforms for developers, and increases computing accessibility for retail users. The platform will serve as core infrastructure for industries that need real-time computation, from autonomous driving to smart cities.
1. AI: From the Age of Productivity to the Age of Production
AI technology has reached a turning point. It is no longer just a tool that boosts human productivity. Now, AI can perform meaningful work with only minimal human guidance, generating independent value. Today’s AI agents can analyze complex scenarios, make autonomous decisions and perform advanced tasks. Agents can produce in-depth reports and program at the level of senior developers.
Once considered the distant future, now this is just the beginning of the disruption. At CES 2025, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang stated, “AI technology is redefining how every industry fundamentally operates.” Huang suggested AI will transform business operations, reshape value creation and impact major aspects of daily life.
2. The Challenges of AI: Stability, Accessibility, and Cost
AI adoption has surged in line with technological leaps. OpenAI’s ChatGPT reached 100 million monthly active users (MAU) within just two months of its launch. This achievement marks the fastest growth rate among other applications. This growth trend extends beyond initial user interest. The continued momentum goes beyond a temporary trend and demonstrates a fundamental shift in our use of technology.
However, the widespread adoption of AI tools among consumers puts significant strain on existing power infrastructure. Large-scale language models (LLMs) require significant computing resources, and high user traffic can often lead to service outages. OpenAI’s service availability heatmap from the past three months shows frequent congestion.
To meet the rising demands of AI usage, companies and governments are expanding data center infrastructure. Projects like the Stargate initiative in the U.S. are examples of this trend. However, centralized systems alone cannot sustain AI operations. As usage grows, existing servers experience increased strain. Additionally, users located far from data centers encounter slower response times, which degrades performance.
Cost is another major challenge. Training and operating AI models require substantial investment, making it difficult to establish sustainable business models. For example, Deepseek, which initially gained traction with low pricing, recently increased its API fees fivefold. Similarly, OpenAI continues to operate at a loss, relying on external funding to maintain operations.
Centralized infrastructure cannot resolve these core challenges. The industry requires a more distributed approach. Bless provides a decentralized solution that addresses the critical issues in today’s AI landscape. By utilizing distributed edge computing, Bless has created a scalable and efficient infrastructure capable of meeting the growing demand for AI services. This decentralized model improves accessibility, lowers costs, and delivers more reliable AI solutions for an expanding market.
3. Bless Network: A New Computing Paradigm for the AI Era
Bless, founded by alumni of Binance Labs and Akash Network, has raised $8 million in seed funding. The project is developing a distributed edge computing network tailored to the increasing demands of the AI era. Currently, Bless operates a testnet built on Solana, which has already garnered over 2.7 million users.
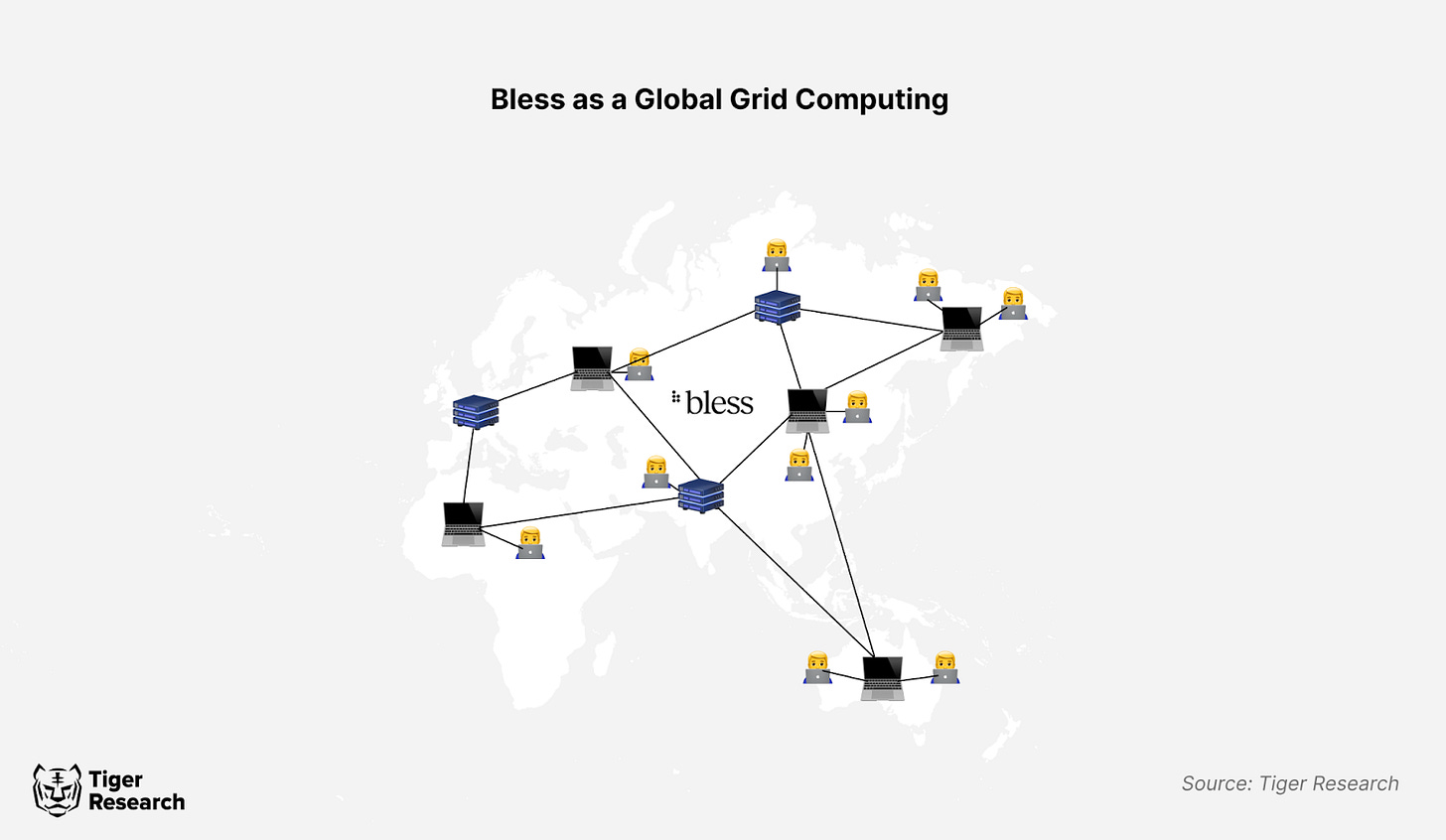
Bless leverages idle computing power from everyday devices like MacBooks and PCs. The network taps into community computing resources instead of relying on centralized data centers. It handles diverse tasks including AI inference, data processing, and web hosting. The system distributes workloads based on device capabilities. High-performance devices run AI model training while others manage simpler processing tasks. Developers gain access to a transparent, stable, and cost-effective computing environment. This decentralized approach serves as a scalable and flexible computing infrastructure for anyone who needs it.
4. Clear Incentive Structure for Distributed Computing Infrastructure
Bless provides clear incentives through its tokenomics model. Node operators receive Bless tokens for providing idle computing resources. Service users purchase computing resources with these tokens based on their needs.
The platform distributes 90% of user-paid tokens to node operators. From this revenue, 10% goes to the treasury. Another 10% from the revenue pool supports network value stabilization through buybacks and token burning. This transparent economic structure creates clear incentives for participants, fostering sustainable growth and expansion of the network.
Web3-based tokenomics provides an ideal framework for building distributed computing infrastructure. Unlike traditional centralized cloud systems bound by corporate and regulatory constraints, Bless builds an open, token-based network that welcomes global participation. This decentralized approach operates independently of national regulations, allowing users to access computing resources without the limitations of centralized payment systems.
Bless allows anyone to participate without requiring specialized equipment or technical expertise. As personal devices continue to improve in performance, contributing to the network becomes even easier. This design attracts more participants as it enables users to earn steady income through rewards. Over time, this structure has the potential to evolve into a Universal Basic Income (UBI) model.
5. Three Key Advantages of Bless: Cost, Stability, and Security
5.1. Stability: Dynamic Management Through Automatic Orchestration
Bless ensures stable infrastructure through automatic orchestration. The system analyzes network status in real-time to assign tasks to the most suitable nodes. This approach is similar to Uber’s ride-sharing model. While traditional taxis have limited response capabilities from fixed locations and vehicles, Uber optimizes driver assignments based on real-time demand and traffic conditions. Similarly, Bless delivers reliable services by leveraging globally distributed user devices rather than relying on centralized infrastructure.
Bless optimizes task allocation by evaluating factors such as workload type, node performance, historical reliability, current status, and geographic proximity. It assigns long-running processes to highly stable nodes and places serverless functions on nearby nodes to ensure faster execution and reduced latency.
Bless improves network efficiency and security through advanced techniques. It uses simulated annealing, an optimizing technique, to evaluate node response times and hardware performance. Additionally, it employs a mathematical method called Greco-Latin square distributions to randomly allocate workloads across multiple nodes, preventing manipulation and enhancing network security.
Automatic Orchestration also enables rapid failover. A geolocation-aware gateway and a continuous health-check system monitor node performance in real time. When a node fails, the system reassigns workloads instantly to the nearest available qualified node, minimizing downtime. Bless guarantees sub-second failover, redistributing tasks within 800 milliseconds to ensure uninterrupted service.
5.2. Cost Reduction: Economic Benefits of Idle Resource Utilization
Bless offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional cloud services by leveraging distributed edge computing. Conventional cloud services require significant investment in data centers. Companies must build physical infrastructure, manage facilities, and ensure a continuous power supply. These fixed costs increase service fees for end users.
Bless, however, reduces costs for end users by using idle computing power from personal devices and promises sustainable delivery through Automatic Orchestration – as explored in the previous section. This model eliminates the need for data center construction and lowers operational costs to approximately 10% of traditional cloud expenses.
Managed cloud services have streamlined IT operations, but the growing demand for AI computing power presents new challenges. According to IDC (International Data Corporation), global public cloud spending is projected to reach $805 billion in 2024 and double by 2028. To stay competitive, businesses must adopt cost-effective solutions.
Bless provides a scalable and affordable alternative. The improving technical capabilites of personal devices lead to an increase in the potential supply of idle computing resources – and in turn strengthen the decentralized, sustainable infrastructure that will underpin the AI era.
5.3. Security: WASM-Based Isolation Environment
Security is of critical importance to distributed computing. Systems must block malicious code and protect developer code and data. Bless addresses these risks with a WebAssembly (WASM)-based secure runtime environment.
Bless’s WASM security framework works like a bank vault. Developers (customers) store code and data in the WASM environment (vault). Node operators (bank employees) perform tasks but cannot access these deposits, ensuring strict security.
Additionally, WASM optimizes performance and protects business logic through ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation and bytecode obfuscation. It secures runtime data with in-memory encryption. WASM provides TEE-like security through software-based isolation. This approach eliminates dependency on hardware-based isolation systems like Intel SGX (Software Guard Extensions) or AMD SEV (Secure Encrypted Virtualization).
This security environment ensures transparent AI agent operations. Since code runs in isolation, the system verifies that AI agents function autonomously without human intervention. As Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) technology advances, this security framework will become even stronger.
6. Exploring New Possibilities in Distributed Edge Computing
6.1. Addressing Blockchain's Infrastructure Centralization
Currently, the blockchain ecosystem depends heavily on centralized cloud infrastructure. Most blockchain validators run on AWS, Google Cloud Platform, or Microsoft Azure. Decentralized applications (dApps) also operate on the same centralized platforms. These services offer stability but conflict with blockchain’s core principle of decentralization.
Bless provides a solution to this issue with a geographically distributed node network that strengthens security and stability, with additional outage protections. More participants increase the level of decentralization and improve network resilience. This model supports both blockchain validators and dApp developers, offering a more independent and scalable infrastructure.
6.2. An Efficient Development Platform for Developers
Bless provides developers with an efficient development environment through distributed edge computing by applying a local-first approach to run tasks on nearby nodes. This method reduces latency and improves service stability. Netflix’s CDN (Content Delivery Network) follows a similar model to ensure smooth streaming for global users.
Bless CLI provides everything you need from managing projects to handling deployments. Developers deploy websites or frontend applications to Bless' infra using a single command. The platform provides testing and monitoring capabilities. WASM runtime environment supports Python, JavaScript, Go, Rust and other programming languages. Developers code freely in their preferred languages.
Bless offers Functions, a serverless computing environment similar to AWS Lambda. Triggers automate tasks based on network and on-chain events. These features deliver a flexible and efficient development environment.
6.3. New Possibilities for Retail Users
Demand for high-performance computing is growing rapidly. In many cases, advanced AI models—like Deepseek’s 70B+ model—require more power than personal computers can handle. Bless’s distributed infrastructure gives users quick and easy access to these LLMs.
Bless also has strong potential in the gaming industry. As game graphics advance, players need high-performance hardware. Bless uses distributed computing to provide high-quality rendering at a lower cost. It offers a viable alternative.
Furthermore, users can share their computing power and earn income. This creates new economic opportunities in the digital era.
7. Bless: Expansion into Global Computing Grid
Bless supports more than AI. The network could support autonomous driving, smart cities, and medical diagnostics, where real-time processing is critical. These industries require low-latency computing, making edge computing more effective than monolithic data centers. Bless meets this demand with a flexible distributed architecture that aims to become a key infrastructure for advanced industries.
Bless is expanding to meet growing demand. With over 2.7 million nodes registered, the network now supports 800,000 daily active users (DAU) through a Chrome extension.
Bless plans to introduce three new node types:
Desktop Nodes: Standalone applications for long-running workloads.
CLI Nodes: Docker-based solutions for institutions and professional operators.
Nestled Nodes: Opt-out nodes that automatically contribute computing power to supported applications whenever the applications are opened by the user.
Nestled Nodes enable effortless network expansion. Users do not need to install anything, and computing power scales automatically as more users access supported applications. This model follows Bless’s Network-Neutral Application (nnAPP) paradigm.
The system connects devices like MacBooks, PCs, and servers as distributed nodes in real-time, enabling instant access to computing resources worldwide. This eliminates regional limitations and lays the foundation for a global computing grid. Bless aims to create a universal infrastructure capable of supporting computing needs in various high-tech sectors.
8. Closing Thoughts
The AI era demands infrastructure that can handle soaring workloads. Data centers alone cannot meet this need, especially when cost and latency issues persist. Bless tackles these challenges by leveraging idle resources in a decentralized model.
This approach goes beyond a technical fix. It prioritizes accessibility and fair distribution of computing power to reduce the global computing gap. Much like the internet expanded access to information, Bless aims to expand access to AI on a global scale. This vision opens new possibilities for a more inclusive AI-driven future.
🐯 More from Tiger Research
Read more reports related to this research.Disclaimer
This report was partially funded by Bless Network. It was independently produced by our researchers using credible sources. The findings, recommendations, and opinions are based on information available at publication time and may change without notice. We disclaim liability for any losses from using this report or its contents and do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. The information may differ from others' views. This report is for informational purposes only and is not legal, business, investment, or tax advice. References to securities or digital assets are for illustration only, not investment advice or offers. This material is not intended for investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn't harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research's reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state 'Tiger Research' as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo(Black/White). If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.