This report was written by Tiger Research, analyzing Maple Finance's position as an on-chain asset management platform and the strategic opportunities in the evolving crypto institutional market.
TL;DR
As institutional investors increasingly enter the cryptocurrency market, demand is rising for asset management solutions that meet traditional financial standards. Maple Finance has emerged to fill this gap, establishing itself as an on-chain asset management platform.
Maple does more than just connect lenders and borrowers. It conducts structured assessments of borrowers and strategically manages collateral, allowing it to function more like a traditional asset manager. More recently, Maple has expanded its offerings with a Bitcoin yield product, which turns Bitcoin from a passive holding into a yield-generating asset.
As institutions increasingly enter the crypto space, well-prepared asset management platforms like Maple Finance are positioned to secure early institutional relationships—an advantage that could translate into long-term market leadership.
1. The Need for Asset Management in the Crypto Market
In traditional finance, investors with large holdings often rely on brokerage firms for specialized asset management services—a widely adopted strategy. But consider a different case: suppose you’re Michael Saylor, CEO of Strategy, and you've acquired significant Bitcoin holdings. How do you manage those assets effectively?
At first, options like staking or direct lending may seem viable. But in practice, managing large-scale crypto assets is complex and risk-prone. It often requires specialized personnel and robust operational controls. One might instead consider professional asset management, similar to traditional finance. Yet here lies another challenge: structured and reliable asset managers are scarce in the crypto market.
This gap presents a clear opportunity in crypto asset management. Applying proven models from traditional finance to digital assets could unlock significant market potential. As institutional participation in crypto grows, the need for professional, structured asset management is becoming essential.
This demand is becoming more pronounced as institutional participation in crypto accelerates. A key example is Strategy’s large-scale Bitcoin purchases beginning in 2020. Momentum increased further following the approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the U.S. and Hong Kong in 2024.
As a result, a market once dominated by retail investors is approaching its limits. The current environment requires professional asset management solutions tailored to institutional needs.
Maple Finance was created to meet this demand. Founded in 2019, Maple combines traditional financial expertise with blockchain infrastructure, and has steadily established itself as a leading on-chain asset management provider.
2. Onchain Asset Management: Maple Finance
Maple Finance’s structure is straightforward and well-defined. It facilitates credit-based on-chain lending by connecting capital providers (LPs) with institutional borrowers.
This raises a key question: in traditional finance, asset management typically involves diversifying a client’s portfolio across equities, bonds, real estate, and other instruments to manage risk and grow value over time.
In that context, can a platform that exclusively intermediates lending be considered a true asset manager?
The answer becomes clearer when looking at Maple Finance’s actual operations. The platform employs professional asset management practices that extend beyond simple loan facilitation. It conducts thorough credit assessments of institutional borrowers and makes strategic decisions about capital allocation and lending terms.
Throughout the lending process, Maple also engages in active capital management, using mechanisms such as collateral staking and re-lending. This operational model clearly goes beyond basic lending intermediation, aligning more closely with the functions of a modern asset manager.
3. Maple Finance’s Core Participants and Operational Mechanism
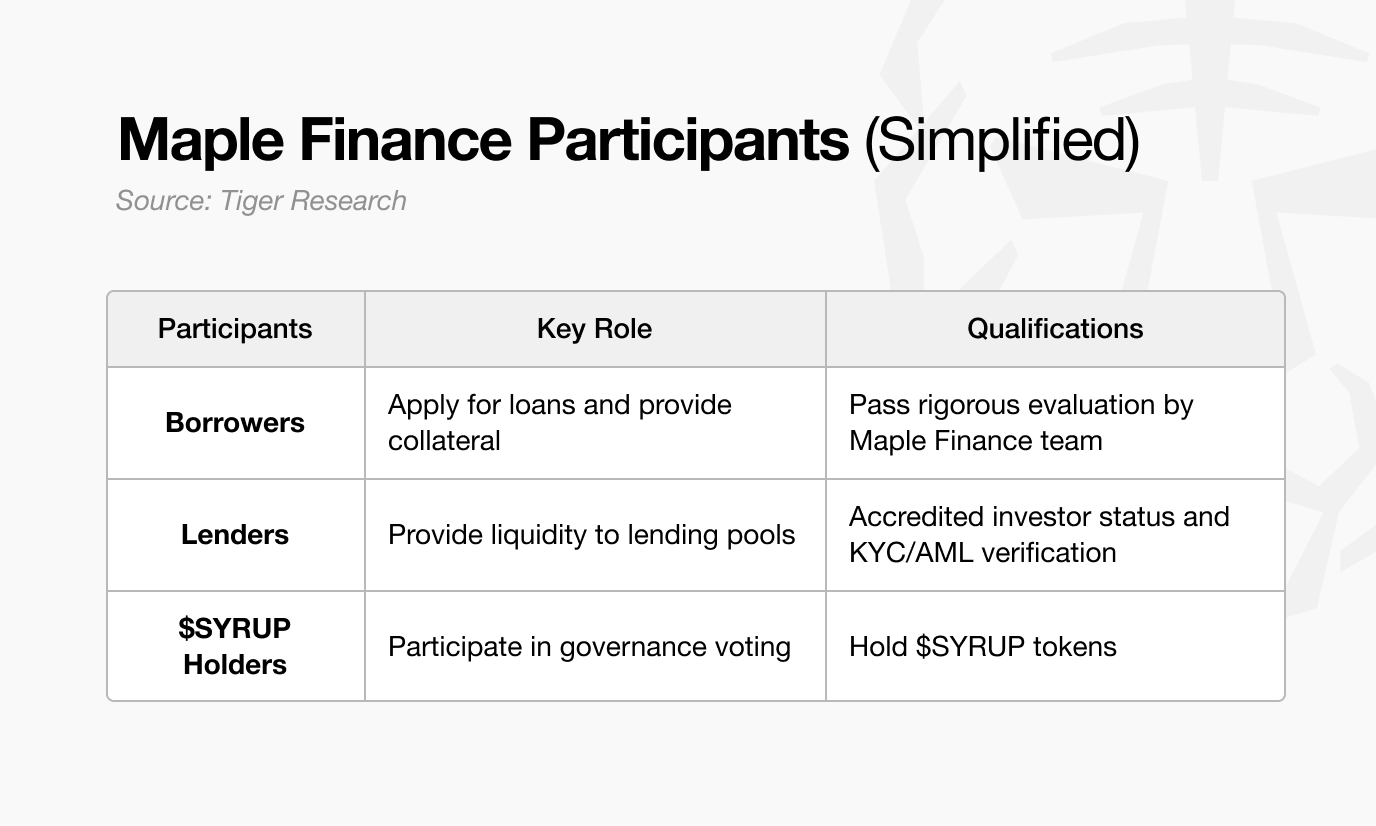
Maple Finance's capacity to function as an on-chain asset management, rather than simply a lending intermediary, derives from its clearly defined participant structure and systematic operational framework. Maple's products are centered around three key participant roles:
This structure mirrors the established safeguards found in traditional finance. In corporate lending at banks, depositors supply capital, companies request loans, and internal credit teams assess financial health. Shareholders, in turn, are involved in governance decisions that shape institutional direction.
Maple Finance operates in a similar manner. When borrowers request a loan, Maple’s credit team sets the terms based on collateral ratios and asset quality. Lenders supply capital, functioning like depositors, while $SYRUP holders take on a governance role similar to shareholders, participating in protocol-level decision-making.
A key distinction is that $SYRUP holders also receive staking rewards funded by protocol revenue. Notably, 20% of revenue is allocated to buybacks, which support these rewards.
Consider a specific example. TIGER 77, a major market maker, needs $10 million in operational funds to expand trading positions amid increased market volatility. However, traditional banks reject the request, citing limited trust in the cryptocurrency sector—leaving TIGER 77 without access to needed capital.
Maple Direct, the in-house lending and advisory arm of Maple Finance, addresses this gap through its High-Yield Corporate Product. Accredited investors, confident in Maple Direct’s performance, deposit $10 million USDC into the lending pool.
When TIGER 77 applies for a loan, Maple Direct conducts a comprehensive credit assessment, reviewing the firm’s financials, operational history, and risk profile. After evaluation, it approves a $10 million USDC loan, secured by Ethereum collateral, at a 12.5% interest rate.
Once the loan is executed, revenue distribution begins. TIGER 77 pays monthly interest, from which Maple Direct retains 12% as a management fee. The remaining interest is distributed to qualified investors.
Here, Maple’s differentiation becomes clear. It goes beyond basic loan intermediation by actively managing collateral—including secondary lending and collateral staking to enhance capital efficiency. In some cases, Maple also structures loans based on corporate guarantees from parent entities rather than traditional collateral.
In effect, Maple offers services comparable to traditional financial institutions. It actively manages capital rather than simply connecting lenders and borrowers. This approach reinforces Maple’s positioning as a credible institutional-grade asset manager, rather than just another DeFi lending platform.
4. Maple Finance’s Key Products
4.1. Maple Institutional
Maple Finance has positioned itself as a legitimate on-chain asset manager by offering a diverse and structured product portfolio. Its offerings fall into two primary categories: lending products and asset management products, each designed to align with different levels of investor risk tolerance and return objectives.
The first category—lending products—includes Maple’s Blue Chip and High Yield offerings. The Blue Chip product line is designed for conservative investors focused on capital preservation. It accepts only established assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum as collateral and follows strict risk management practices.
By contrast, the High Yield product targets investors seeking higher returns and willing to accept greater risk. Its core strategy involves actively managing over-collateralized assets—through staking or secondary lending—to generate additional yield, rather than simply holding the collateral.
Maple Finance’s second product category—asset management—begins with its BTC Yield offering. Launched earlier this year, the product aligns with rising institutional demand for Bitcoin. Its value proposition is simple: rather than passively holding Bitcoin, institutions can deposit BTC to earn interest, generating yield from existing assets.
This naturally raises a question: if institutions can buy and hold Bitcoin directly, why not manage it themselves? The answer lies in practical constraints—chiefly, a lack of technical infrastructure or operational expertise to safely generate yield.
Maple Finance's Bitcoin Yield product utilizes a dual staking provided by the Core DAO. Under this model, institutions securely store their Bitcoin with institutional-grade custodians such as BitGo or Copper, earning staking returns in exchange for committing not to move their assets for a predetermined period. Put simply, institutions safely lock away their assets and earn yield.
However, the process is more complex in practice than it appears. Behind the simplicity of “earning yield on Bitcoin” lies a series of technical and operational steps—contractual arrangements with custodians, participation in Core DAO staking, and conversion of $CORE staking rewards into cash. Each step requires specialized knowledge, which most institutions do not possess in-house.
This mirrors a familiar pattern in traditional finance. While companies can manage assets directly, they often rely on professional asset managers to do so efficiently and securely. In crypto, the need for such expertise is even greater—given the added layers of technical complexity, regulatory oversight, security, and risk management.
Starting with the Bitcoin Yield product, Maple Finance plans to expand into a broader range of asset management offerings. This strategy is critical in bridging the gap between institutional investors and the crypto market, addressing a long-standing unmet need.
By offering comprehensive, professionally managed services, Maple allows institutions to pursue stable returns from digital assets—without diverting focus from their core operations.
4.2 syrupUSDC
The products discussed so far primarily target accredited investors, limiting access for general retail participants. To address this, Maple Finance introduced syrupUSDC and syrupUSDT—retail-focused liquidity pools built on Maple’s existing lending infrastructure and borrower network.
Capital raised through syrupUSDC is lent to institutional borrowers from Maple’s Blue Chip and High Yield pools, who undergo the same credit evaluation process as with other Maple products. Interest generated from these loans is distributed directly to syrupUSDC depositors.
Although the structure resembles Maple’s institutional offerings, syrup pools are managed separately. This design maintains the operational rigor of institutional products while lowering the barrier to entry for retail users—improving accessibility without compromising structural stability.
While yields are slightly lower than those offered to institutional participants, Maple has introduced the “Drips” reward system to enhance long-term engagement. Drips offer additional token rewards, compounding as points every four hours. At the end of each season, points can be converted into SYRUP tokens. Through this incentive mechanism and active capital-raising strategy, Maple Finance has attracted approximately $1.9 billion in USDC and USDT.
In summary, syrupUSDC/USDT extends institutional-grade products to retail investors, combining accessibility with a structured reward mechanism. By integrating Drips, Maple demonstrates a clear understanding of Web3 engagement dynamics, offering a model that encourages sustained participation while preserving financial discipline.
5. Key Differences in Maple Finance
Maple Finance’s core differentiator lies in its implementation of an institutional-grade system fully deployed on-chain. Rather than relying solely on algorithmic lending protocols, Maple combines on-chain infrastructure with human expertise, creating an environment tailored to institutional standards.
5.1. A Service Developed by Traditional Finance Experts
This distinction begins with Maple’s team composition. Many on-chain financial platforms lack professionals with traditional finance backgrounds. While such experience isn’t strictly required, delivering genuinely institutional-grade services is difficult without a deep understanding of institutional investor needs and risk expectations.
This is where Maple stands out. Its team includes professionals with decades of experience in traditional finance and credit evaluation. Their expertise enables rigorous credit assessments and robust risk management, forming the trust foundation institutional clients require.
The background of Maple’s leadership team helps explain its credibility with institutional investors.
CEO Sidney Powell brings asset management experience from National Australia Bank and Angle Finance. Co-founder Joe Flanagan was a consultant at PwC, specializing in corporate financial analysis, and later served as CFO at Axsesstoday.
On the technical side, CTO Matt Collum previously served as a senior engineer at Wave HQ and was the founder of Every, a fintech startup. COO Ryan O’Shea worked in strategy at Kraken, gaining direct experience in the crypto sector.
The broader team includes professionals with backgrounds across both finance and technology. Sid Sheth, Director of Capital Markets, worked in institutional sales at Deutsche Bank. Steven Liu, Head of Product, held product management roles at Amazon and led fintech initiatives at Anchorage Digital.
Maple’s core strength lies in this blend of traditional finance and blockchain expertise. The team’s dual-domain knowledge enables them to meet institutional expectations while delivering on-chain solutions with operational credibility and technical precision.
5.2. Differentiated Risk Management System
Maple Finance’s risk management approach reflects the expertise of its professional team and sets it apart from most DeFi protocols. While most protocols rely heavily on automated, decentralized mechanisms, Maple applies proven methodologies from traditional finance directly on-chain.
The first critical component is the loan assessment process. In most DeFi protocols, loans are issued automatically upon collateral deposit, with little to no credit evaluation.
Maple Finance, by contrast, implements a more deliberate underwriting model. As described earlier, borrower screening is conducted by Maple Direct, its investment advisory arm. This credit-first approach, combined with a preference for overcollateralized structures, enables Maple to manage risk from the outset.
In situations requiring liquidation, most protocols trigger immediate asset sales once collateral falls below a threshold. Maple takes a different approach—issuing a 24-hour notice that gives borrowers the chance to replenish collateral. This mirrors traditional banking practices, where margin calls precede liquidation. If the borrower does not respond within the window, liquidation proceeds.
Even the liquidation process itself is designed to minimize market impact. While common DeFi protocols conduct liquidations openly on exchanges—risking slippage and price disruption—Maple executes liquidations via pre-arranged OTC deals with market makers, ensuring controlled execution and reduced volatility.
Maple’s withdrawal system also stands out. In traditional DeFi, users can withdraw funds instantly if liquidity is available—but uncertainty arises when it’s not. Maple processes withdrawals sequentially or in timed batches, giving users clear expectations on fund availability. This structured approach allows investors to plan effectively, adding certainty and confidence to Maple’s risk management framework.
5.3. Integrated Ecosystem Structure
Maple Finance adopted a measured approach to growth—prioritizing internal risk management and strategic alignment over rapid expansion. Before engaging in external partnerships, the team established a robust risk framework. Rather than scaling indiscriminately, Maple focused on collaborating with core partners where synergy could drive meaningful value creation.
This strategy is clearly reflected in the expansion of the syrupUSDC ecosystem. To broaden its reach within DeFi, Maple partnered with leading platforms such as Spark and Pendle, enabling diversified yield structures and multiple access points for users.
The collaboration with Spark delivered concrete results: Spark allocated $300 million to syrupUSDC, using it as collateral backing for USDS. This was not a symbolic partnership—it resulted in real capital deployment.
The integration with Pendle further enhanced flexibility. syrupUSDC holders can now tailor their yield exposure using Pendle’s Principal Token (PT) and Yield Token (YT) mechanisms. This model—leveraging each partner’s specialized strengths—has become a consistent strategy across Maple’s products.
The BTC Yield product reflects the same approach. Its goal: to turn Bitcoin from a passive holding into a yield-generating asset. Achieving this required two core components: secure custody and productive deployment. Maple addressed both—partnering with BitGo and Copper for institutional-grade custody, while generating yield through Core DAO’s dual staking model. The result is an integrated system where custody and yield coexist without tradeoffs.
6. Maple Finance in 2025 and Beyond
In December 2024, Maple Finance released its strategic roadmap in a founder’s letter outlining priorities for 2025. Roughly six months later, many of these objectives have already been met:
Maple’s TVL surpassing $4 billion;
First TradFi partner to lend $100m+ through Maple Institutional;
First $100m+ DeFi integration for Syrup.fi; and
Protocol revenue crossing $25m+
Maple’s long-term vision is ambitious. By 2030, the platform aims to manage $100 billion in annual lending volume—a nearly 45x increase from its current portfolio of $2.2 billion. Achieving this scale will require more than expanding existing lending operations. Maple must broaden its asset management product suite, deepen partnerships with traditional financial institutions, and attract a global base of institutional investors.
The first strategic focus is expanding adoption of the BTC Yield product. Institutional interest in Bitcoin has surged, alongside demand for solutions that generate returns beyond simple custody. Capturing a significant share of this market will be essential.
The second strategy involves broadening Maple’s asset offerings. Currently focused mainly on Bitcoin, Maple plans to extend yield-generating products across various digital assets. Recently, institutional investors have begun adding Ethereum to their portfolios, and this trend toward diversified digital asset holdings is expected to accelerate. If Maple can offer effective asset management services that generate additional yield from these assets, significant growth opportunities will arise.
7. Maple Finance: Positioned for Greater Prominence
The cryptocurrency market has historically been retail-driven. As of now, total market capitalization stands at approximately $3.29 trillion (CoinMarketCap)—still modest compared to $51 trillion in U.S. Treasury bonds and $18–27 trillion in gold. These comparisons underscore the growth potential if crypto becomes fully integrated into traditional asset classes.
Institutional investors will play a central role in driving this growth. Unlike retail participants, institutions manage assets in the billions or tens of billions, meaning even incremental allocations can significantly expand the crypto market. However, institutional entry comes with higher expectations—including regulatory compliance, sophisticated risk management, and secure custody solutions.
Maple Finance is specifically positioned to serve this institutional segment. Rather than offering basic lending tools, Maple has built a comprehensive suite of financial services designed to meet institutional standards. Its strategy now includes expanding partnerships and contractual relationships with traditional financial institutions to further strengthen credibility.
A recent milestone highlights this positioning: Maple announced the first tranche of a Bitcoin-backed financing facility with Cantor Fitzgerald. Cantor’s Bitcoin financing division plans to provide up to $2 billion in initial financing, with Maple selected as the first borrower. This underscores Maple’s institutional credibility and leadership in the crypto credit market.
Winning high-profile clients—such as Strategy, which has adopted Bitcoin as a treasury asset—would further accelerate Maple’s adoption of its BTC Yield product. The timing is especially critical: institutional clients are sticky. Unlike retail customers, institutions rarely change service providers once established, preferring long-term partnerships for risk and operational continuity.
Maple is not the only firm pursuing this market, but its proven institutional track record gives it a strong advantage. Ultimately, the next two to three years will be decisive in determining which platforms emerge as category leaders in institutional crypto finance.
🐯 More from Tiger Research
Read more reports related to this research.Hyperlane: The Permissionless Cross-Chain Protocol Connecting 150+ Blockchains
The Open Gaming Manifesto: How B3 Will Save the Web3 Gaming Industry
Chromia's Vector Database: A Pioneering Convergence of AI and Blockchain
Disclaimer
This report was partially funded by Maple Finance. It was independently produced by our researchers using credible sources. The findings, recommendations, and opinions are based on information available at publication time and may change without notice. We disclaim liability for any losses from using this report or its contents and do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. The information may differ from others' views. This report is for informational purposes only and is not legal, business, investment, or tax advice. References to securities or digital assets are for illustration only, not investment advice or offers. This material is not intended for investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn't harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research's reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state 'Tiger Research' as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo following brand guideline. If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.