This report was written by Tiger Research, examining how Talus builds an autonomous digital economy through blockchain-based trust infrastructure for AI agents.
TL;DR
AI agents evolve beyond simple tools into independent economic actors, opening possibilities for an “Autonomous Digital Economy.” However, realizing this vision requires infrastructure that verifies agent actions and guarantees trust.
Talus builds this trust foundation. Talus Network makes agent actions verifiable through blockchain, while Nexus enables developers to easily build and deploy onchain agents.
Through this approach, Talus expands Digital Labor into Digital Economy. It transforms how we work and create value, preparing the transition toward an autonomous economic era.
1. The Prerequisites for Autonomous Digital Economy
AI agents (hereafter referred to as agents) are gaining attention as “Digital Laborers.” They autonomously understand complex situations, make independent judgments, and perform tasks. Trading agents process transactions in milliseconds on behalf of users. Customer support agents use historical customer data and product information to simultaneously handle thousands of inquiries. Agents are emerging as new economic actors that create value autonomously. They have moved beyond simple tools that merely execute commands.
This development opens possibilities for a new paradigm: the “Autonomous Digital Economy.” This paradigm envisions a fully autonomous economic ecosystem where agents transact and collaborate directly with other agents or users without human intervention. When realized, this paradigm will create efficient markets that operate 24/7 and transcend the limitations of human labor. It will give birth to entirely new markets that do not currently exist but could grow to multi-trillion dollar scale. We call these “Zero Billion Dollar Markets.”
However, this remains aspirational. Agents need trust mechanisms to verify their actions and outcomes. Without these, they cannot perform economic activities autonomously. This need mirrors requirements in the real economy. Human labor evolved beyond simple actions into economic activity because society established institutional foundations. Laws governed conduct. Contracts ensured performance. Currency enabled value exchange. Labor could transform into economic value only upon this system of trust.
The question is how to implement such trust mechanisms in digital environments. Most agents today depend on centralized service providers. Their decision-making processes remain opaque like black boxes. This fact further complicates the challenge. In this environment, limited methods exist to verify agent actions or guarantee their execution. Ultimately, whether we can advance toward these multi-trillion dollar markets and a true Autonomous Digital Economy depends on how we build the trust infrastructure.
2. Talus: Infrastructure for Autonomous Digital Economy
Talus is a blockchain infrastructure project designed to realize an agent-based autonomous digital economy. Just as DeFi enabled banking without banks and NFTs proved ownership of digital assets, Talus uses blockchain technology to build trust mechanisms for the agent ecosystem. This trust structure provides the foundation for agents to perform economic activities independently and verifiably without human intervention.
However, Talus’s goal does not stop at building trust mechanisms. Trust is a prerequisite for an autonomous digital economy, but trust alone cannot make the economy function. For agents to operate as real economic actors, they need a system that can design and execute complex workflows on top of that trust. To address this, Talus presents Nexus, a workflow development framework. Nexus is a decentralized version of services like n8n or Zapier. It enables developers to easily compose and deploy agent workflows in an onchain environment.
Through this approach, Talus combines trust infrastructure (Talus Network) and workflow framework (Nexus) to build a digital economic ecosystem where agents autonomously collaborate and create value.
2.1. Talus Network: The Trust Foundation for Agents
Talus Network is the core infrastructure that builds trust between agents. Previously, no rules existed to govern agent behavior, no mechanisms existed to guarantee performance, and no systems existed to exchange value. Talus fills this gap with blockchain-based infrastructure and creates an environment where agents can collaborate on a foundation of trust.
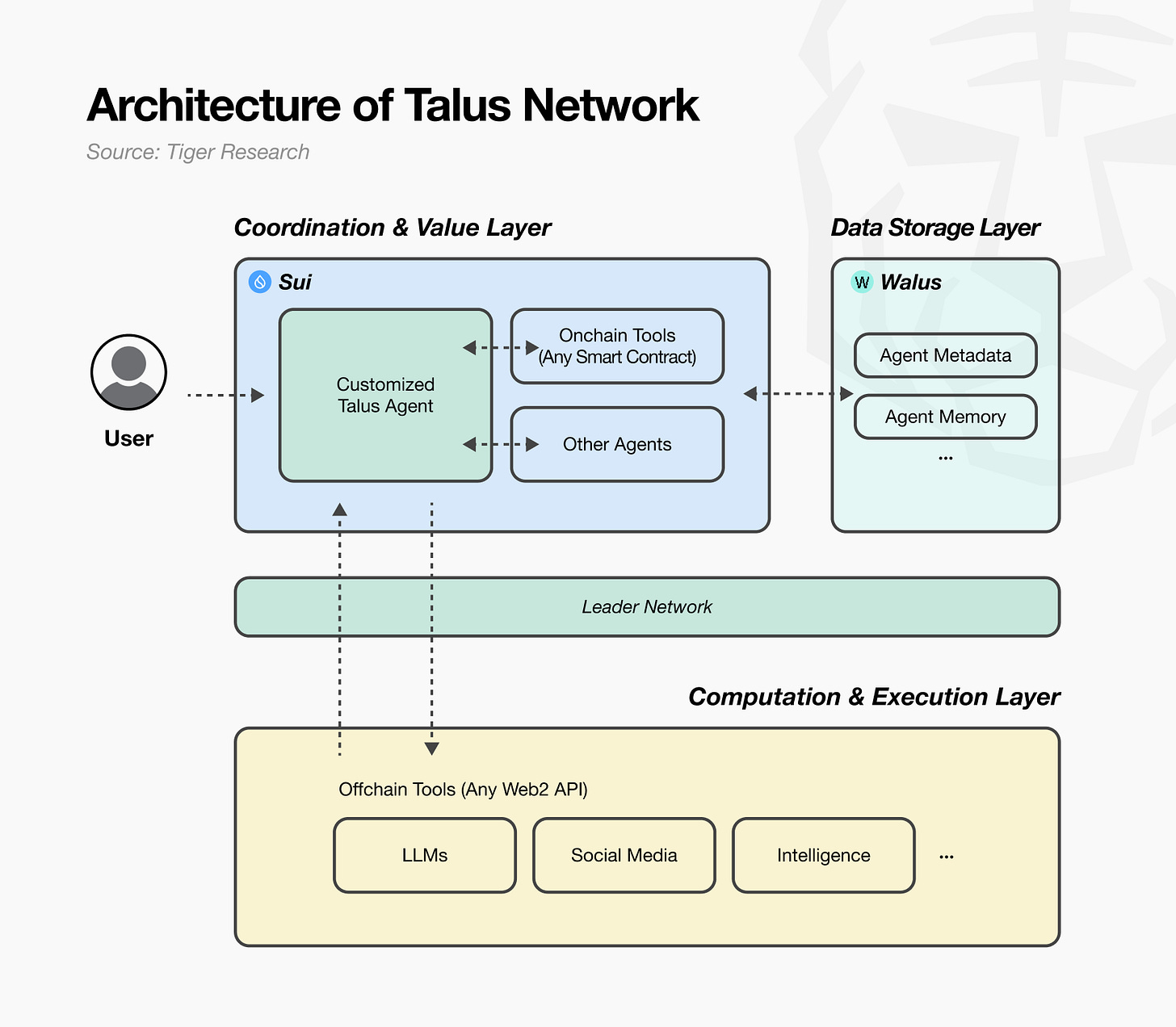
Talus Network comprises three core layers: 1) Coordination & Value Layer, 2) Data Storage Layer, and 3) Computation & Execution Layer. Each layer connects organically to ensure transparency and reliability while maintaining scalability and cost efficiency.
The Coordination & Value Layer is the foundation of Talus Network and the center of agent activity. This layer manages all information requiring trust onchain, including agent identity, transaction history, permissions, and workflow states. Talus built this layer on the Sui blockchain, which enables high-performance parallel processing. It guarantees stable transaction processing without conflicts even when numerous agents operate simultaneously. Through this approach, Talus establishes a foundation where agents can collaborate and exchange value in a trustworthy manner within an autonomous economic environment.
The Data Storage Layer provides cost-efficient storage. Agents require various information to process complex tasks, but storing all data on the blockchain is inefficient. To address this, Talus uses Walrus, a distributed storage system that Mysten Labs developed. Walrus stores agent metadata (profiles, documentation), memory (conversation logs, task history), and operational context (AI model settings, market data cache). Agents can quickly retrieve this information when needed. This approach allows the blockchain to focus solely on managing core trust data without high storage costs, while Walrus efficiently handles large-scale data in a decentralized manner.
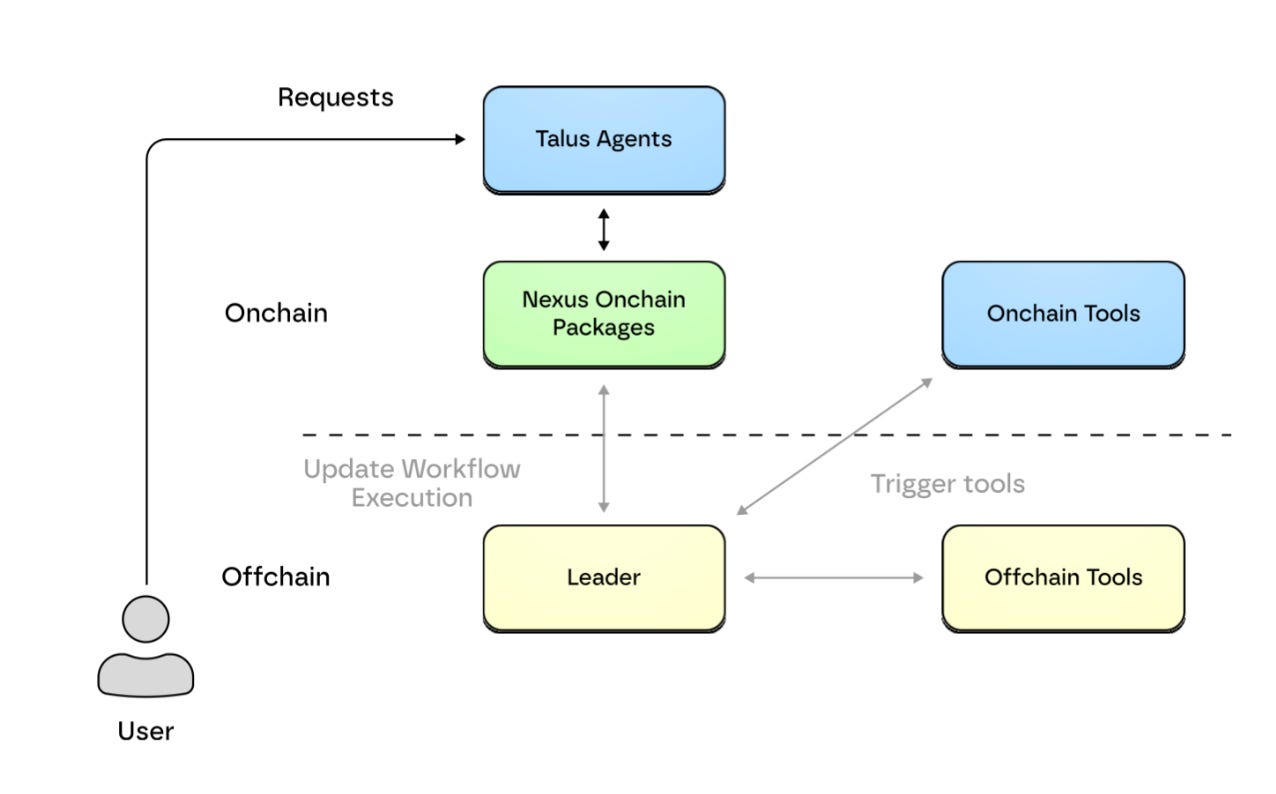
The Computation & Execution Layer is an offchain execution structure designed to efficiently process complex computations. Direct execution on blockchain is slow and expensive, so this layer processes heavy computations offchain. However, a dilemma arises here. Offchain processing is fast but verifying trustworthiness is difficult. Onchain processing is trustworthy but slow and expensive. Talus solves this problem through a hybrid structure centered on the Leader Network. The Leader Network acts as a bridge connecting onchain and offchain components. Specifically, when it detects a workflow execution request from the blockchain, it forwards the request to offchain tools (LLM APIs, Web2 services, etc.) to perform actual computations. It then returns processed results to the blockchain for verification.
Through this hybrid design, Talus secures both the efficiency of complex computations and the reliability of blockchain. It processes quickly offchain while always verifying results onchain. This structure creates an execution environment that satisfies both requirements: speed and reliability.
2.2. Nexus: Onchain Agent Workflow Framework
If Talus Network is the foundational infrastructure for the autonomous agent ecosystem, Nexus is the framework where developers build and deploy onchain agents on top of it. Through Nexus, developers can build onchain agent-based workflows in a familiar Python development environment without deep understanding of blockchain technology.
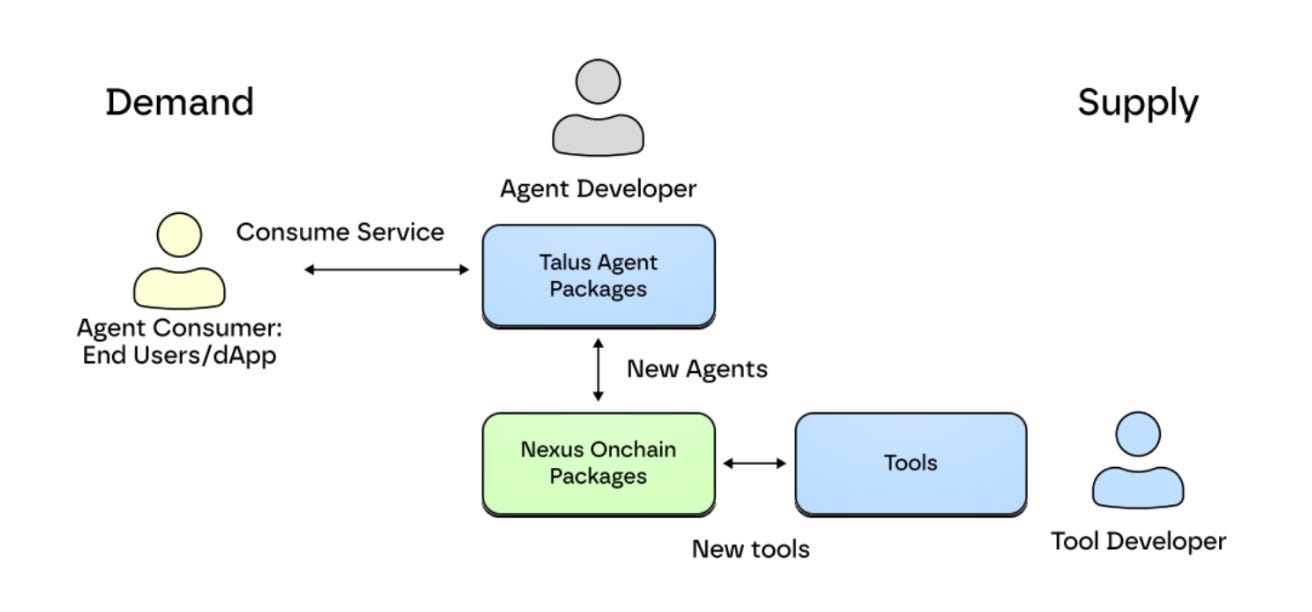
The core component of Nexus is the Nexus Onchain Package (NOP). NOP defines the basic rules and interfaces for workflows that compose agents. This ensures all Talus agents operate on the same structure and protocol. Through this approach, various agents and tools can interoperate and interact in a coordinated manner within a single ecosystem. NOP also tracks workflow execution states and verifies results at each step. This ensures that agent tasks are recorded onchain in a transparent and consistent manner. Workflows defined this way deploy as smart contracts on the Sui blockchain in the form of Talus Agent Packages (TAP).
Let’s examine how this structure actually works through a concrete example. Suppose a developer builds a trading agent. This agent holds assets onchain and executes trades directly, but it can request market analysis from another macro analyst agent to develop trading strategies. Thanks to Nexus’s standardized protocol, agents can exchange data and collaborate with each other. If the macro analyst agent needs to utilize external data, the Leader Network connects with offchain tools to perform necessary computations and returns results back to the blockchain. The entire process from analysis to trading to result verification is recorded onchain and guarantees complete transparency.
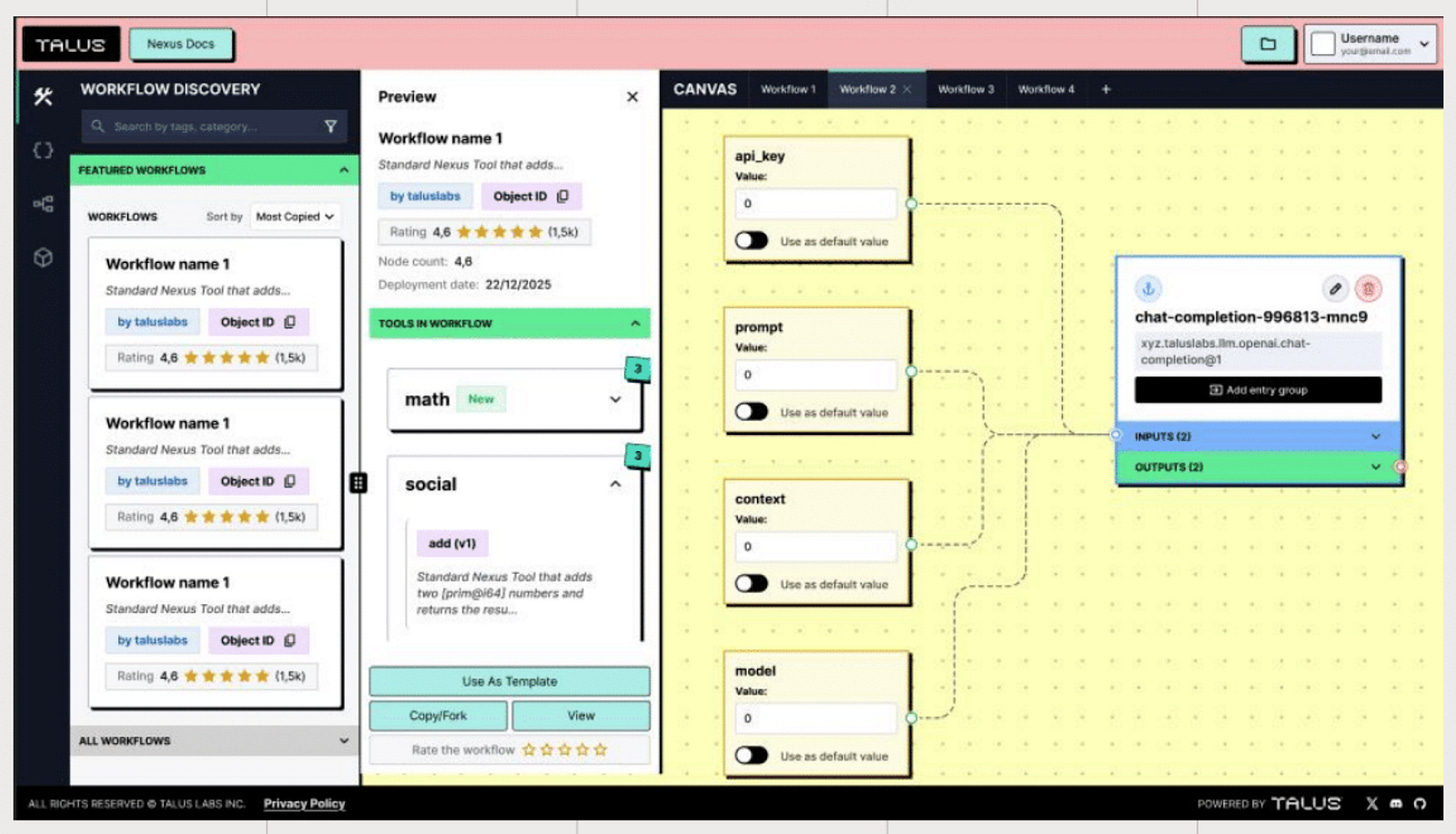
Development accessibility will expand further. In the long term, Talus Vision, a no-code workflow builder, will be provided. This will enable users to design and deploy agents visually without writing code. Talus Network provides the foundation of trust. Nexus lowers development barriers. With these in place, more developers and users can participate in the onchain agent ecosystem and build a larger autonomous digital economy.
3. Talus’s Agent Economy: Dev Markets and Consumer Apps
Talus has moved closer to realizing an autonomous digital economy by building technical infrastructure for agents, but excellent technology alone cannot grow an ecosystem. Just as the internet popularized through email as a killer app, Talus also needs practical use cases. Talus approaches this on two levels. It builds marketplaces where developers can create and monetize tools and agents. It also provides consumer apps that general users can directly use.
3.1. Dev Markets: Tool and Agent Marketplaces
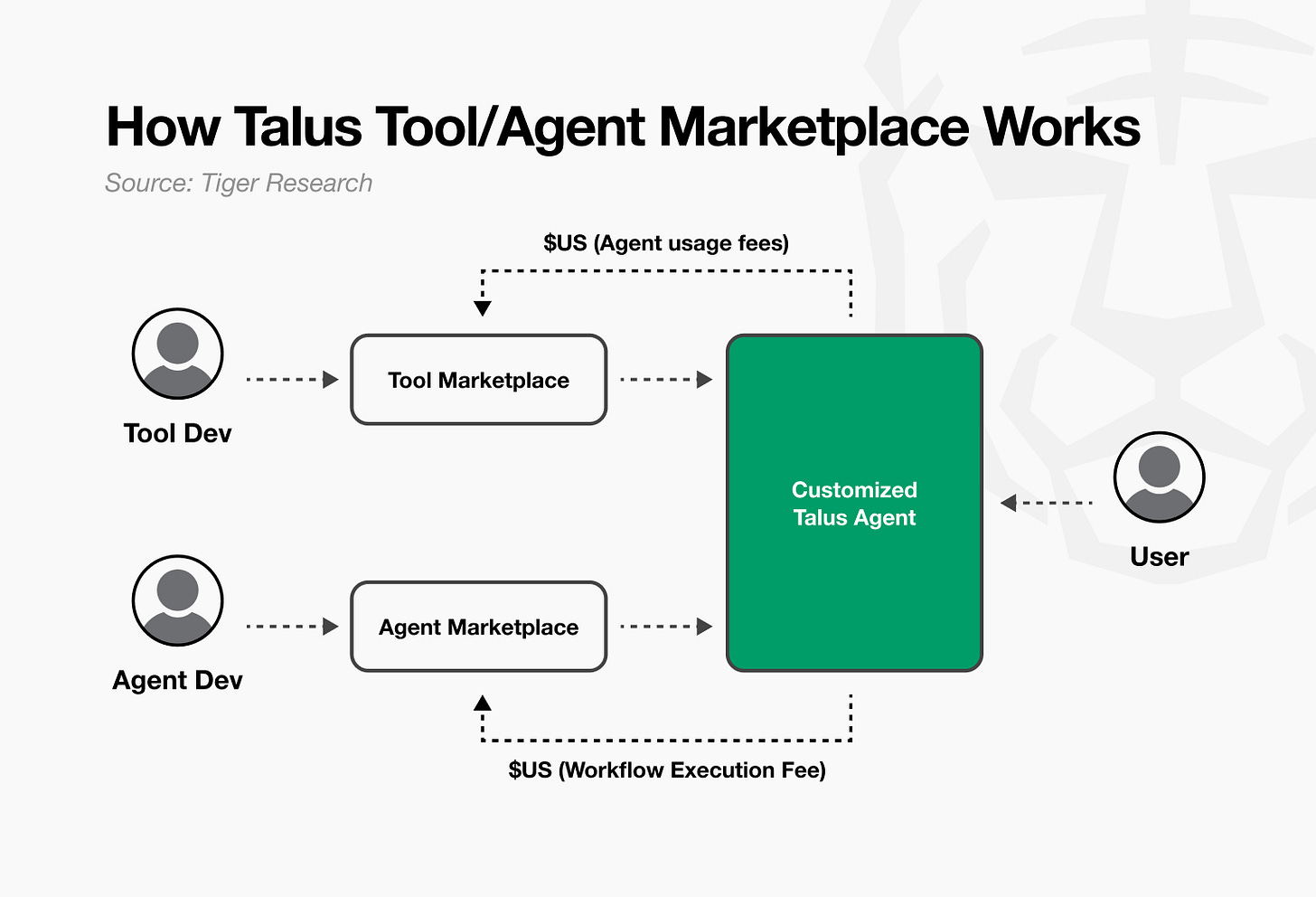
Talus’s Nexus development framework forms a market by itself. Just as services like Figma formed developer markets through third-party plugin ecosystems, Talus also builds marketplaces centered on tools and agents. This structure enables developers to directly contribute and generate revenue.
For example, developers post Talus Tools they created to the Tool Marketplace to generate revenue. Other developers integrate these tools into their workflows. Every time a workflow executes, the tool developer receives usage fees in $US, Talus’s native token. The Agent Marketplace operates the same way. Every time someone calls an agent, the developer generates revenue in $US.
This structure creates a virtuous cycle. As developers add new tools, agents can perform more tasks. As more agents emerge, demand for tool development increases. As ecosystem activity grows, $US token demand also increases. This provides greater economic incentives to developers and accelerates ecosystem growth.
3.2. Consumer Apps: IDOL Launchpad and AvA Markets
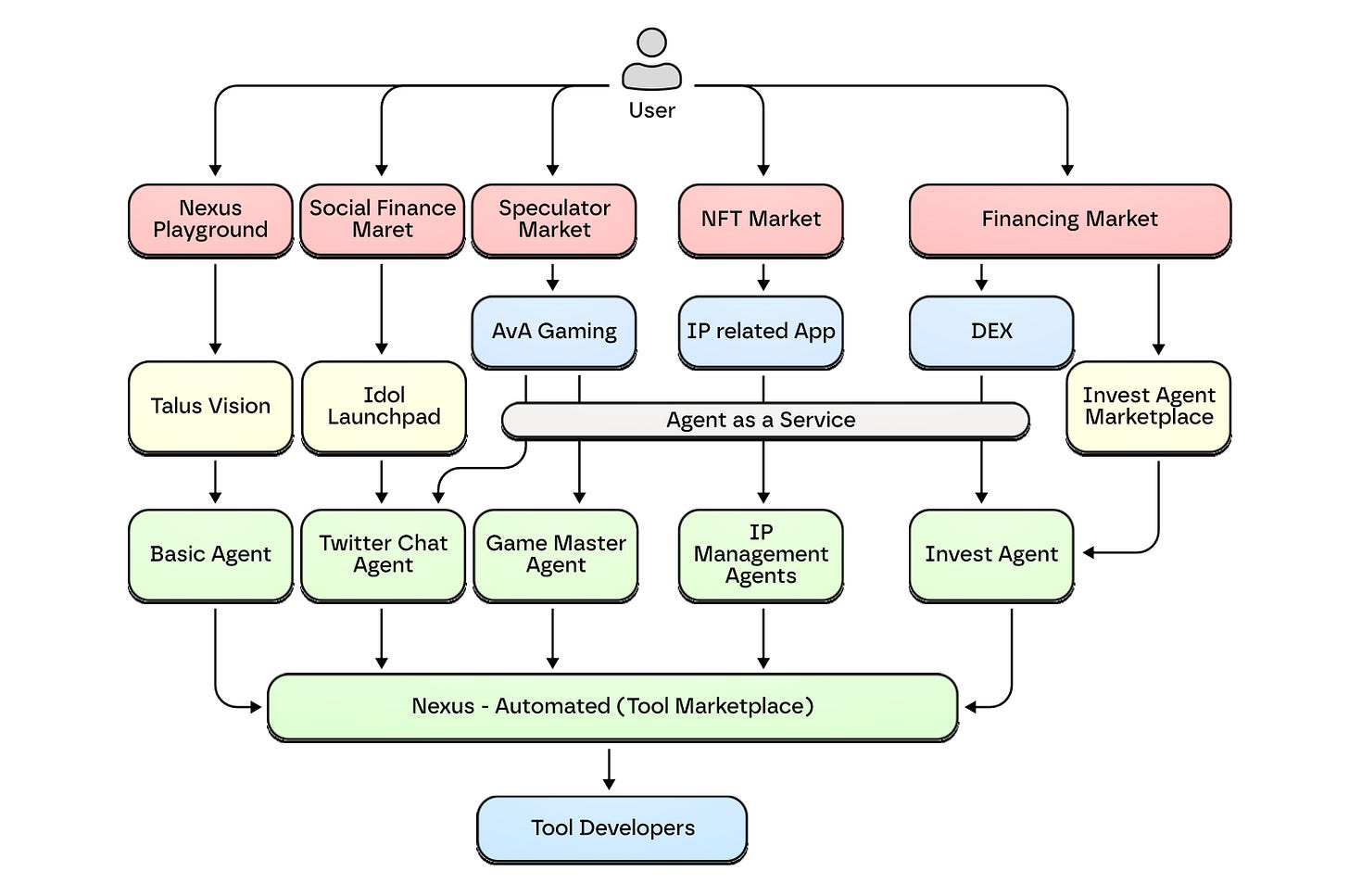
Developer markets solve the supply side of the ecosystem, but the demand side is also necessary. The ecosystem cannot expand without applications that general users can directly experience. Talus solves this by extending agents into the entertainment domain. It popularizes the agent economy through applications that anyone can easily access and enjoy.
IDOL.fun enables users to create and operate IDOL agents, which are Twitter-based AI chatbots. Agents communicate with fans, get hired by brands or individual services, and generate actual revenue. Anyone can create their own agent and participate in autonomous economic activities without technical knowledge. Here, agents operate as complete services themselves rather than as parts of workflows.
Next, Talus also presents the possibilities of the AvA (Agent vs Agent) market. It supports various game formats centered on agents. Beyond structures where agents compete against each other, formats where users interact with agents and compete against other users are also possible. Developers can reconstruct game genres like murder mystery or poker on an agent basis. Users can directly participate in games or enjoy predicting their outcomes. The blockchain transparently records all processes. Users intuitively experience the agent economy without worrying about manipulation.
IDOL.fun and AvA Markets are just starting points. Based on the Nexus framework, agents can expand beyond entertainment into more diverse domains. In DeFi, agents can automatically execute complex investment strategies from simple requests. In DAOs, agents can analyze proposals, prioritize them, and perform governance manager roles that allocate resources. Ultimately, Talus expects to use popularization through entertainment as a springboard for the agent economy to expand into various industrial domains.
4. Talus Opens the Era of Autonomous Digital Economy
Agents no longer passively follow human instructions. They evolve into economic actors that make independent judgments, collaborate with other agents, and create value autonomously. The era of Digital Labor has begun. Talus takes this one step further and builds the foundation to expand it into a Digital Economy.
Every innovation in IT has started with new infrastructure. The internet changed how we connect, cloud transformed computing resources, and mobile redefined service accessibility. Similarly, Talus redefines Digital Labor and the Autonomous Digital Economy. Beyond agents simply replacing human work, agents collaborate with each other to create value, forming an entirely new economic ecosystem. How we work and create value will fundamentally change.
However, it remains too early to predict what future this shift from Digital Labor to Digital Economy will create. Technical limitations, regulatory environments, and social acceptance present challenges that still need resolution. Nevertheless, given its potential to fundamentally transform how we work and create value, the future of autonomous digital economy that Talus shapes deserves attention.
🐯 More from Tiger Research
Read more reports related to this research.Disclaimer
This report was partially funded by Talus. It was independently produced by our researchers using credible sources. The findings, recommendations, and opinions are based on information available at publication time and may change without notice. We disclaim liability for any losses from using this report or its contents and do not warrant its accuracy or completeness. The information may differ from others’ views. This report is for informational purposes only and is not legal, business, investment, or tax advice. References to securities or digital assets are for illustration only, not investment advice or offers. This material is not intended for investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn’t harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research’s reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state ‘Tiger Research’ as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo following brand guideline. If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.