As Bitcoin falls, attention shifts to DAT companies that hold the largest volumes of BTC. Strategy is one of the most visible players in this group. The key questions are how the firm accumulates its assets and how it manages risk as market volatility increases.
Key Takeaways
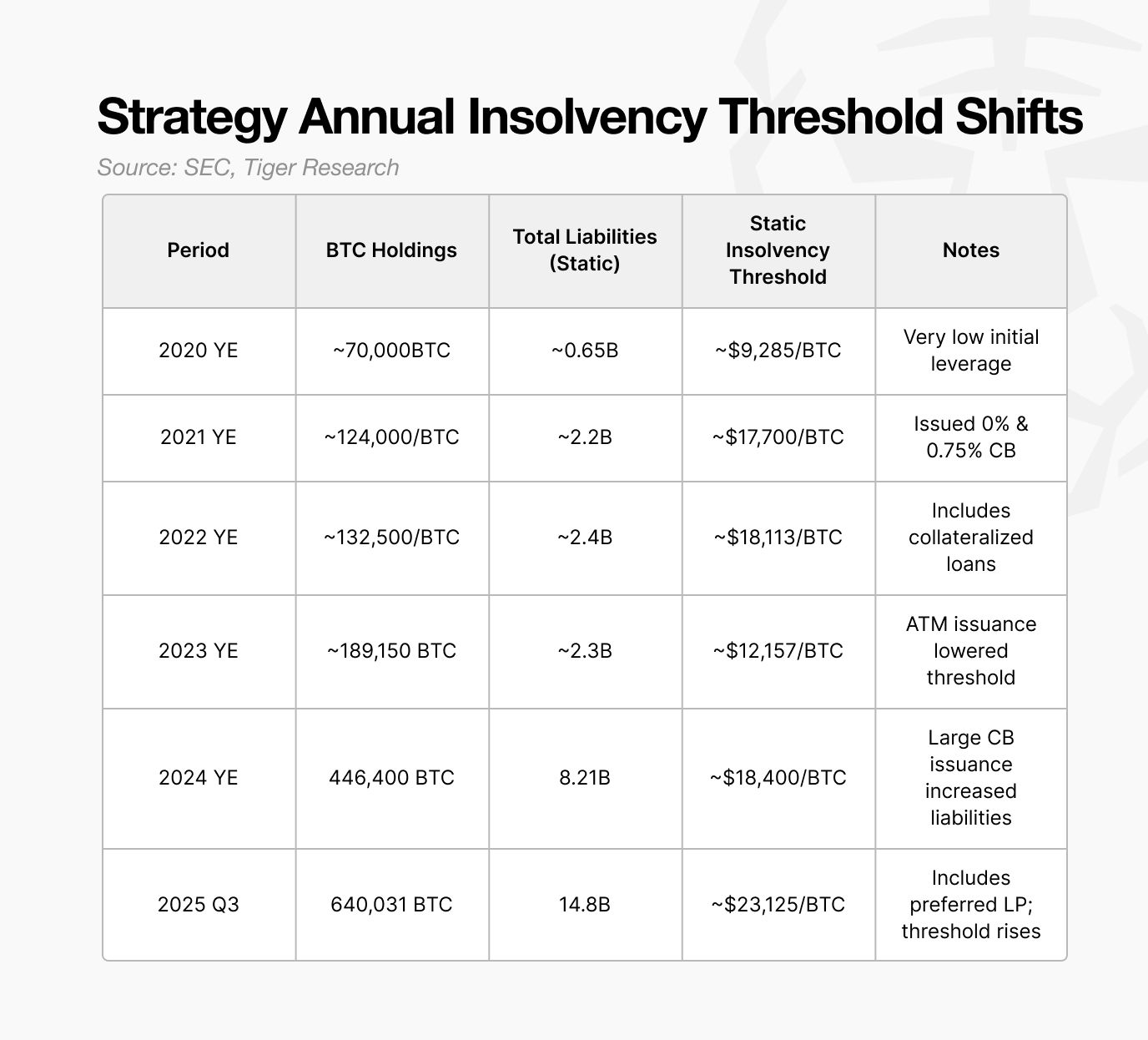
Strategy’s static bankruptcy threshold is estimated at about $23,000 in 2025, nearly double the $12,000 level in 2023
The firm shifted its capital-raising model in 2024 from simple cash and small convertible notes to a diversified mix of convertibles, preferred equity, and ATM issuance
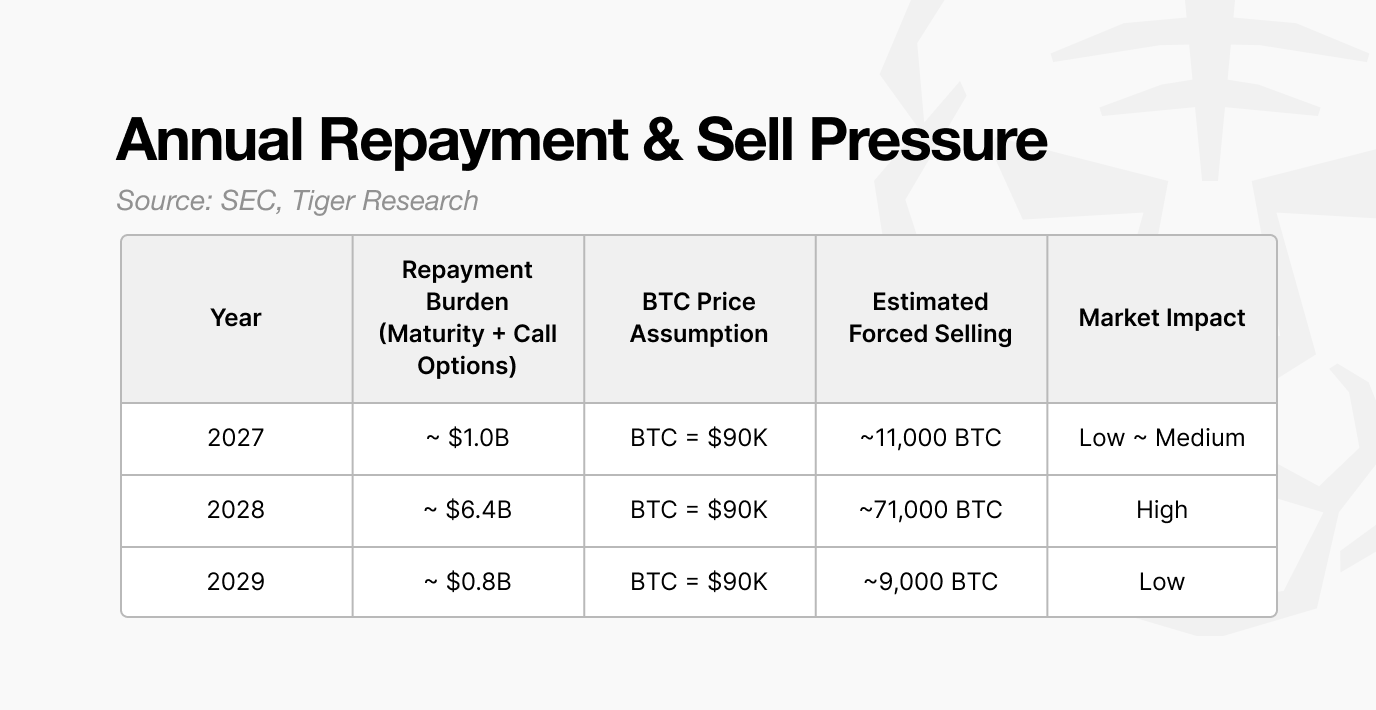
The call option held by investors allows early redemption before maturity. If Bitcoin prices fall, investors are likely to exercise this option, making 2028 a critical risk window
If refinancing fails in 2028, Strategy may need to sell roughly 71,000 BTC, assuming Bitcoin at $90,000. This represents about 20 to 30 percent of average daily trading volume and would create material market pressure
1. Questions Around Strategy’s Stability
The recent drop in Bitcoin pushed DAT company stocks down by roughly 50 percent. This raised a central question in the market: with both the share price and the firm’s core asset falling, is Strategy still on stable ground. The concern intensified after JPMorgan noted that Strategy could be removed from the MSCI index.
The attention is not only about the stock. Strategy holds a Bitcoin position large enough to influence the broader market, well beyond the scale of a typical whale. This leads to two key questions.
At what Bitcoin price does Strategy’s balance sheet break
When and under what conditions could the firm create market impact
This report reviews SEC filings to identify Strategy’s effective bankruptcy threshold, the periods in which its risk increases, and the potential market implications if stress scenarios occur.
2. Is Strategy at Risk: The $23,000 Threshold
Before moving into the analysis, we clarify the concept of static bankruptcy. Static bankruptcy occurs when a company would be unable to repay its liabilities even if all assets were liquidated.
Put simply, static bankruptcy occurs when assets are smaller than liabilities. For example, if Echo owns a house worth 1 billion won and 100 million won in cash but owes 1.2 billion won, the firm is insolvent on a balance sheet basis. DAT companies face the same condition. If Bitcoin falls below a certain level, book equity turns negative and the firm becomes unable to meet its obligations. This level is referred to as the static bankruptcy threshold.
To identify Strategy’s static bankruptcy threshold, we first examine how the firm accumulated its Bitcoin holdings.
Strategy has held Bitcoin as a strategic asset since 2020, but its accumulation model changed after 2023. Until then, the firm relied on cash reserves and small convertible notes to purchase Bitcoin. Holdings remained in the low 100,000 BTC range, and refinancing obligations were limited.
From 2024, the funding approach shifted. Strategy increased leverage by combining preferred equity issuance, an ATM stock program, and large convertible offerings to finance additional Bitcoin purchases.
This led to a rapid acceleration in Bitcoin accumulation. The structure created a loop in which higher Bitcoin prices raised the firm’s market capitalization, enabled greater leverage, and supported further purchases.
The goal remained the same, but the funding mix and risk profile changed. This structural shift is now a central factor elevating Strategy’s bankruptcy risk.
Strategy’s estimated static bankruptcy level for 2025 is roughly $23,000. Below this level, the value of its Bitcoin holdings falls below its liabilities, making the firm insolvent on a balance-sheet basis.
A key point is that this threshold has been rising. In 2023, the firm could withstand Bitcoin at about $12,000. The threshold increased to $18,000 in 2024 and reached $23,000 in 2025. As Strategy expanded its Bitcoin position, the critical level moved higher.
The $23,000 threshold therefore represents the minimum Bitcoin price required for stable operations. It implies that Bitcoin would need to decline about 73 percent from current levels to trigger insolvency risk.
3. Convertible Bonds: The Issue Is the Holder Put, Not the Maturity
As noted earlier, Strategy’s static bankruptcy threshold rose to $23,000 because liabilities grew faster than Bitcoin holdings. The next question is how this debt was structured.
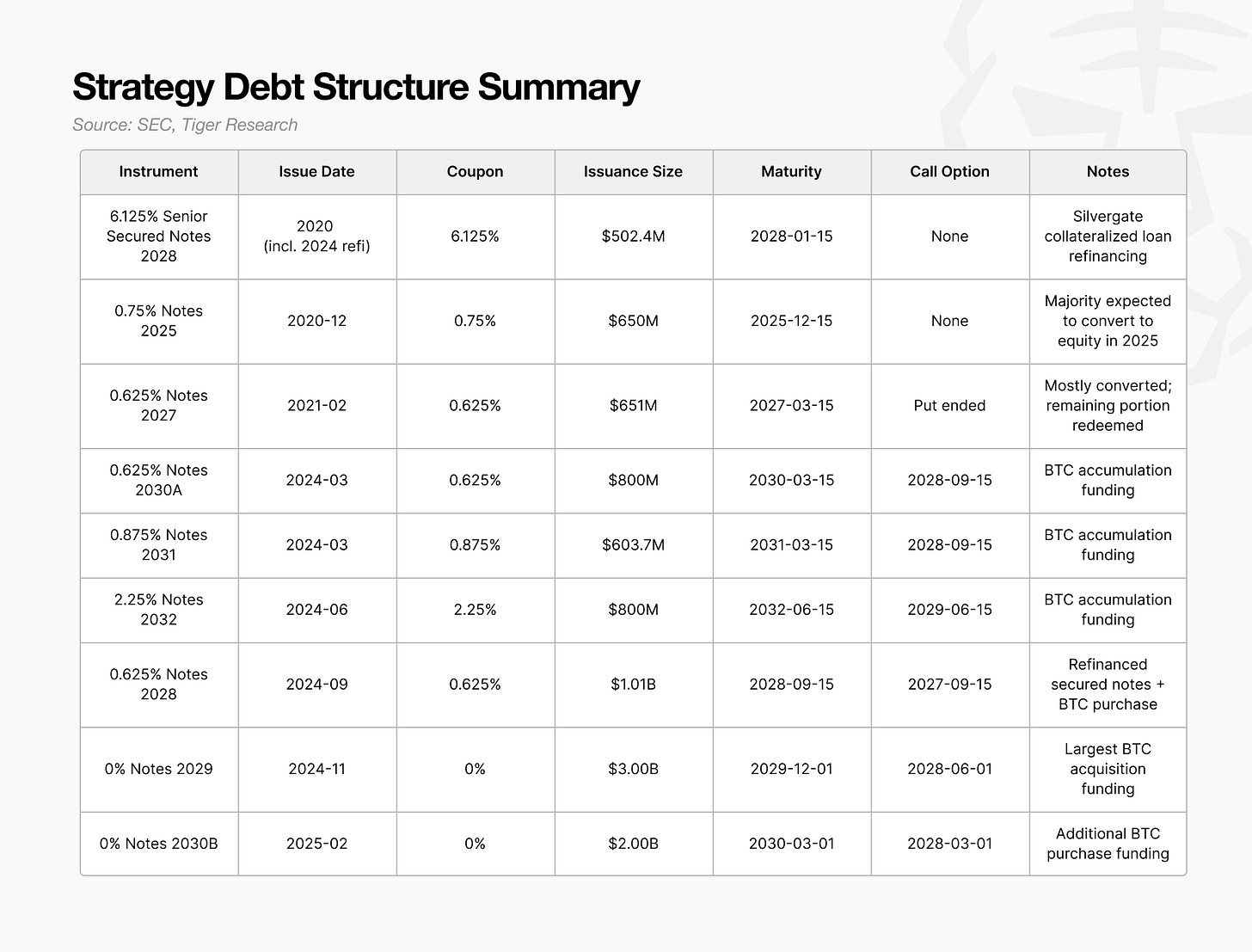
Between 2024 and 2025, Strategy adopted a new capital-raising model that combined convertible bonds, preferred equity, and an ATM stock program. Among these instruments, convertible bonds account for the largest portion and have the most significant market impact.
The key point is not the size or maturity of the convertible issuances. What matters is the timing of the holder put.
This provision allows investors to demand early repayment, and the company cannot refuse. Most of the large convertibles issued in 2024–2025 cluster around a 2028 holder put date, making 2028 the critical year in which Strategy must demonstrate its refinancing capacity.
If Bitcoin prices approach the bankruptcy threshold in 2028 or market conditions deteriorate, investors are likely to exercise the put rather than wait for maturity. A wave of put exercises would require Strategy to raise several billion dollars in cash immediately.
The challenge is that the capital raised through these convertibles was used almost entirely to buy Bitcoin. Had the funds been deployed into productive assets that generate cash flow, the firm would have a natural source of repayment. Instead, the focus on Bitcoin accumulation leaves little cash available for redemption.
As a result, repayment would need to come from asset sales. If Bitcoin prices are low when the put window opens, Strategy could face an immediate liquidity shortfall. Forced selling would push prices lower, further raise the bankruptcy threshold, and potentially set off a negative feedback loop.
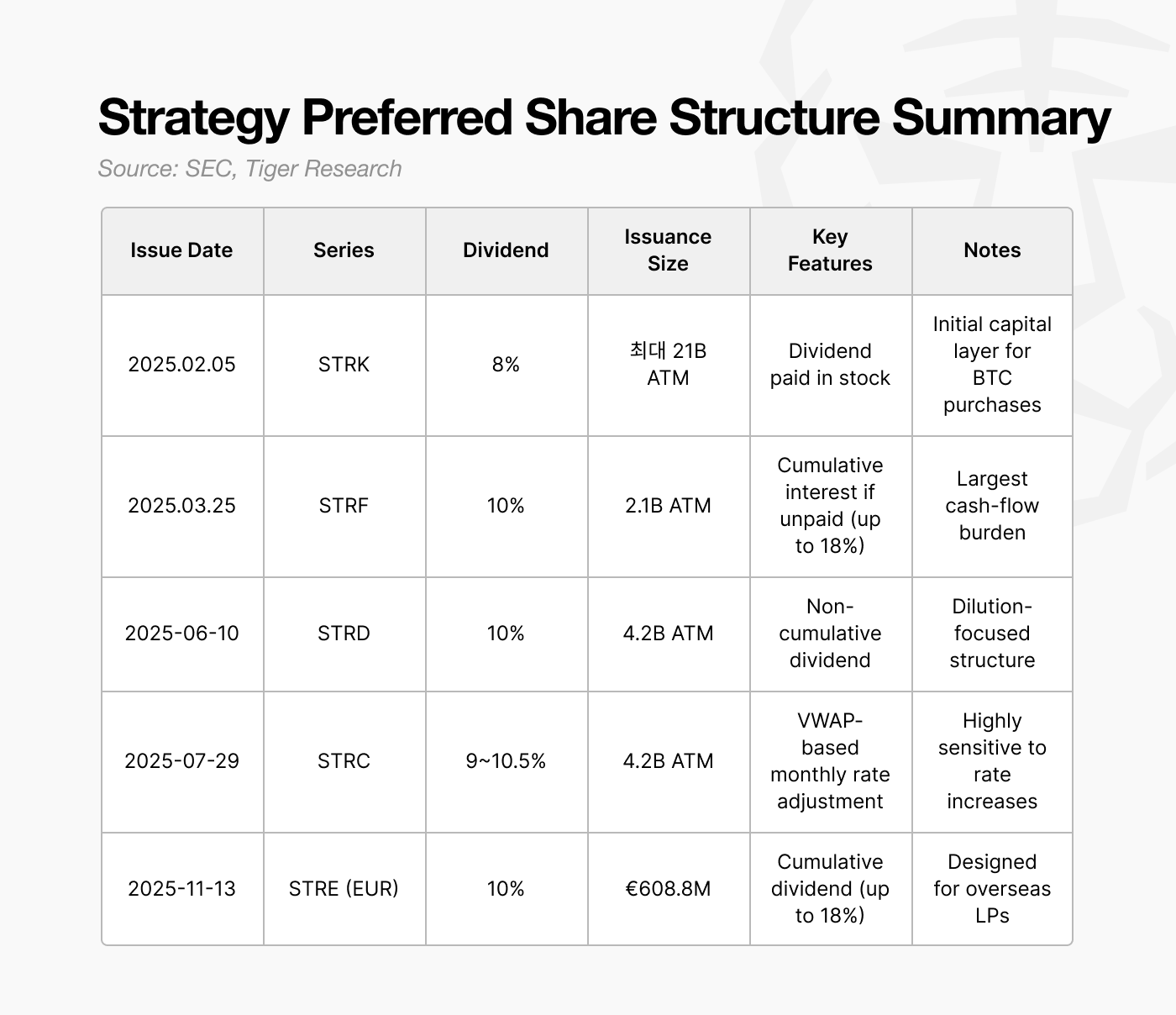
4. Preferred Equity: Why Choose a 10 Percent Dividend Burden
Starting in 2025, Strategy shifted from issuing near-zero-coupon convertible bonds to issuing preferred equity with roughly a 10 percent dividend. At first glance, this appears to be a far more expensive choice.
The decision, however, reflects the mounting refinancing pressure in 2027–2028. The clustering of holder put in 2028 significantly increases mid-term repayment risk. Any sustained cash outflow during this period would raise insolvency risk.
The key feature of preferred equity is that dividends do not need to be paid in cash. Strategy structured the issuance so that dividends can be paid in shares when needed. This allows the firm to raise capital without immediate cash leakage and to meet dividend obligations without using cash. In effect, preferred equity helps the firm avoid selling Bitcoin during the critical 2027–2028 period.
Although a 10 percent dividend rate seems expensive, the ability to pay in shares makes it a tool for preserving liquidity and preventing short-term cash failure.
The structure, however, introduces new challenges. Paying dividends in stock creates ongoing dilution for common shareholders. Strategy already faces potential dilution from future conversion of convertible bonds, and preferred equity adds another source of equity pressure.
Preferred equity also carries priority claims. If the firm faces simultaneous pressure from debt repayments and operating costs, preferred holders must be serviced before common shareholders. While preferred equity has no fixed maturity, its dividend obligation functions as a structural fixed cost and contributes to the firm’s effective bankruptcy threshold.
By 2024–2025, Strategy had moved away from a model built on low-cost convertibles to a blended structure of convertibles, preferred equity, and ATM issuance. This shift enabled rapid expansion of Bitcoin holdings in the short term.
5. What Happens If Strategy Fails
If Strategy is unable to refinance in 2028, the impact on the market can be estimated through its repayment obligations.
The large convertibles issued in 2024–2025 create roughly 6.4 billion dollars of potential repayments in 2028. If market conditions weaken and preferred issuance, ATM issuance, and new convertibles all become unavailable, the firm would have no option but to sell Bitcoin.
Assuming Bitcoin at 90,000 dollars, Strategy would need to sell about 71,000 BTC to meet these obligations. This is not comparable to a typical institutional sale.
Current spot market volumes average 20 to 30 billion dollars per day. Selling 71,000 BTC at 90,000 dollars equates to roughly 6.4 billion dollars, or about 20–30 percent of daily trading volume. A sale of this magnitude within a short window would almost certainly create significant price pressure.
The larger concern is that such sales would not be a one-off event. As Bitcoin prices fall, the value of Strategy’s assets declines immediately, weakening its financial ratios. This further restricts its ability to raise capital and can force additional Bitcoin sales.
The result is a negative cycle: refinancing failure leads to forced selling, forced selling drives prices down, declining prices reduce asset value, and the firm is pushed toward further sales. Even a few quarters of this dynamic could deteriorate the balance sheet beyond recovery.
Strategy’s structural risk is therefore concentrated in 2028. Outside this window, the leverage model appears manageable, but failure to refinance in 2028 could trigger selling pressure large enough to affect the broader Bitcoin market.
2028 thus represents a pivotal year, not only for Strategy’s survival but also for potential volatility across the Bitcoin ecosystem.
6. Strategy Is Relatively Stable, but Late Entrants Face Higher Risk
Market narratives often reduce DAT risk to a simple question of whether a firm will survive each Bitcoin drawdown. This analysis shows that survival is determined not by short-term price moves or stock volatility but by the firm’s balance sheet and the design of its capital structure.
Evaluating DAT companies therefore requires more than tracking declines in their share prices or in Bitcoin. Key metrics include the location of their static bankruptcy threshold, the timing of cash repayment pressures, and the instruments chosen to bridge funding gaps. These factors allow a view of structural resilience rather than short-term noise.
Not all risks can be forecast. ETF flows, macro conditions, and regulatory shifts can reshape the environment at any moment. Even so, the most reliable anchors are the bankruptcy threshold implied by the numbers and the firm’s underlying cash flow mechanics.
Strategy stands apart in this respect. It entered Bitcoin in 2020, endured the 2022 downturn, and accelerated accumulation in 2024 through leveraged financing. Its mix of convertibles and preferred equity created a multilayered buffer.
As a result, Strategy has a comparatively stable base. Newer entrants do not yet have a proven DAT framework, and their ability to withstand a major price decline is far less certain.
This report aims to provide a foundation for assessing DAT companies through quantitative signals rather than fear or optimism, and to highlight the structural risks that truly matter.
🐯 More from Tiger Research
Read more reports related to this research.Disclaimer
This report has been prepared based on materials believed to be reliable. However, we do not expressly or impliedly warrant the accuracy, completeness, and suitability of the information. We disclaim any liability for any losses arising from the use of this report or its contents. The conclusions and recommendations in this report are based on information available at the time of preparation and are subject to change without notice. All projects, estimates, forecasts, objectives, opinions, and views expressed in this report are subject to change without notice and may differ from or be contrary to the opinions of others or other organizations.
This document is for informational purposes only and should not be considered legal, business, investment, or tax advice. Any references to securities or digital assets are for illustrative purposes only and do not constitute an investment recommendation or an offer to provide investment advisory services. This material is not directed at investors or potential investors.
Terms of Usage
Tiger Research allows the fair use of its reports. ‘Fair use’ is a principle that broadly permits the use of specific content for public interest purposes, as long as it doesn’t harm the commercial value of the material. If the use aligns with the purpose of fair use, the reports can be utilized without prior permission. However, when citing Tiger Research’s reports, it is mandatory to 1) clearly state ‘Tiger Research’ as the source, 2) include the Tiger Research logo. If the material is to be restructured and published, separate negotiations are required. Unauthorized use of the reports may result in legal action.